
Lung cancer is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers worldwide and is now the most common cause of cancer mortality in the UK, resulting in 21% of all cancer deaths. Only 9.5% of patients diagnosed with lung cancer will live to ten years or more post diagnosis[1].
Lung cancer is split historically by cancer cell morphology into two main types: small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell (NSCLC).
NSCLC is divided into: adenocarcinoma, which develops from mucus-forming tissues; squamous lung cancer, which develops from squamous epithelium; and large-cell carcinoma, which derives from lung epithelium but lacks the features of other types of lung cancer; however, there are rare subtypes[2].
Another malignancy — pleural mesothelioma — develops from mesothelial cells, which form the serosal lining of the pleural cavity[3]. This malignancy is incurable and aggressive and beyond the scope of this article. For those wanting to learn more, a clinical overview of mesothelioma can be found here[4]. Detail on the rates of different cancer morphologies can be seen in Figure 1.
Data suggest that 79% of cases of all lung cancer are preventable; 72% of lung cancer cases are caused by smoking; 13% of cases are caused by occupational exposure (e.g. ceramic or construction industry); and 8% of lung cancer cases are linked to air pollution[5,6].
Environmental carcinogens, such as asbestos and radon, lead to the development of lung cancer. The likelihood increases with the dose and duration of exposure, and these carcinogens act synergistically with smoking, amplifying the risk[7,8].
Several comorbidities — including HIV infection, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) — are associated with an elevated risk of lung cancer[7].
Pharmacists play a role in advising on the most suitable systematic anti-cancer therapy (SACT) agent based upon PD-L1 expression, genetic testing, evidence, adverse effect profile and SACT commissioning. Pharmacists working as non-medical prescribers can review patients on treatment and prescribe their anti-cancer therapy. This is of benefit to expanding the workforce to grow capacity in clinics to review and care for the ever-growing number of people with cancer.
This article will outline the lung cancer screening programme in England and the pilots in Scotland and Wales, how lung cancer is diagnosed, and will provide an overview of the current available treatment options, including the involvement of pharmacy teams where appropriate.
Figure 1 shows types of lung cancer by histology[9].
Symptoms and clinical presentation
Patients diagnosed with lung cancer most often present with cough (50–75% of cases), dyspnoea (25–40%), chest pain (20–40%) and haemoptysis (15–30%); however, some patients may be asymptomatic on presentation and diagnosis. The most common place for patients to present is in primary care but up to 40% of cases may present in a hospital emergency department[3]. Within England, community pharmacy pilots have been set up in various locations to spot patients with early signs of lung cancer (e.g. a new persistent cough) and refer directly to secondary care or diagnostic services[10,11].
Symptoms may arise from the primary tumour, local intrathoracic spread, distant metastases and paraneoplastic syndromes[12,13]. Systemic symptoms — such as weight loss, loss of appetite and fatigue — are also common. The presence of finger clubbing and haemoptysis significantly heightens the suspicion of lung cancer[12].
In cases of intrathoracic spread, symptoms vary based on the affected site[14]. Malignant pleural effusion, invasion of the oesophagus and chest wall invasion may lead to symptoms such as increased dyspnoea, dysphagia and pleuritic chest pain, respectively. Recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy can cause hoarseness of voice, while superior vena cava syndrome presents with facial swelling, plethora and upper extremity oedema[12].
Liver metastases can lead to lethargy and weight loss, along with hepatomegaly[14]. Bone metastases may result in bone pain and pathological fractures, while brain metastases can present with headaches, seizures, nausea, vomiting and altered consciousness[15,16].
Paraneoplastic syndromes result from the cancer’s ectopic hormone production or the body’s reaction to the tumour (these are most commonly observed in SCLC)[17]. Hypercalcaemia of malignancy, caused by parathyroid hormone-related peptide, is a life-threatening emergency. Hyponatraemia can occur owing to inappropriate antidiuretic hormone or atrial natriuretic peptide production[14].
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) states that patients who have two or more of these red flag symptoms may have lung cancer and would warrant an urgent X-ray and referral to cancer pathway[18]:
- Deep vein thrombosis;
- Appetite loss — unexplained in ≥40 years and is a previous or current smoker;
- Cough, fatigue, shortness of breath or chest pain or weight loss aged ≥40 years;
- Recurrent chest infections aged ≥40 years;
- Finger clubbing aged ≥40 years;
- Haemoptysis aged ≥40 years;
- Thrombocytosis (high platelet count) aged ≥40 years;
- Lymphadenopathy — where lymph nodes are enlarged these are commonly supraclavicular lymph nodes found above the clavicle (collar bone) in individuals aged ≥40 years[18].
Screening
In England since 2023, lung cancer screening has been incorporated into a comprehensive national programme, specifically targeting individuals at a higher risk for the disease[19]. This initiative focuses on individuals aged 55–74 years, primarily those with a history of smoking, recognising them as a high-risk population. The screening programme uses low-dose CT scans of the lungs, aimed at detecting lung cancer in its early stages when intervention can be more effective[20,21].
Elsewhere in the UK, planning is underway to implement a similar screening programme to the one established in England. In Scotland, lung cancer screening is only being piloted through the ‘LUNGSCOT’ project in the NHS Lothian health board area and has yet to be rolled out nationally[22].
Similarly in Wales, a small pilot is underway in Cwm Taf Morgannwg University Health Board in south Wales[22].
Calculations suggest that if a lung cancer screening programme equivalent to England’s was introduced in Scotland and Wales, it could diagnose around 4,000 more people with lung cancer at an early stage (stage 1 or 2) in Scotland over the next decade, and 2,400 more people at an early stage in Wales[22].
The establishment of these screening programmes follows the success of the ‘SUMMIT’ study, the largest lung cancer screening study in the UK[23]. Designed to detect lung cancer early among at-risk populations, its findings demonstrated the feasibility and effectiveness of early detection but also provided evidence to inform the development of a nationwide lung cancer screening programme[23]. The programme recognises the importance of holistic support by offering smoking cessation assistance to those identified as needing it[23].
Diagnosis and assessment
The diagnosis of lung cancer involves many assessments and evaluations, with the objective of determining the disease’s extent, identifying the target site and to allow tissue biopsy to determine histology and the molecular characteristics[24,25].
Initially, a chest X-ray is carried out, which can detect abnormalities but cannot provide a definitive cancer diagnosis[25].
All patients with suspected lung cancer should undergo a contrast-enhanced CT scan of the chest, abdomen and pelvis[25]. PET/CT imaging offers valuable insights into the tumour’s metabolic activity, aiding in surgical planning[25]. Brain imaging is not done if early-stage disease is suspected (stage I or II) and if the patient shows no neurological symptoms[25].
MRI with contrast is carried out if: the patient has advanced disease (stage III or IV); the patient shows neurological symptoms; or the patient has limited-stage SCLC who are candidates for chemoradiation[25]. A contrast-enhanced brain CT scan is sufficient in patients receiving palliative care who are not undergoing any neurosurgical intervention[25].
Tissue biopsy can be obtained through various methods. For peripheral tumours, CT or ultrasound-guided percutaneous biopsy is often appropriate. Bronchoscopic techniques — such as endobronchial ultrasound-transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) or endoscopic TBNA — are valuable for sampling mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes[25,26].
In cases where needle aspirations are inconclusive, mediastinoscopy may be employed to sample lymph nodes. Video-assisted thoracoscopy surgery (VATS) has largely replaced thoracoscopy and a newer approach, robotic-assisted thoracoscopy (RATS), offers enhanced precision in comparison to VATS[27].
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) has become useful in the determination of the precise histology of the malignancy in the lung and helps to determine the primary site. There are various protocols based upon the cell expression and the IHC helps define the cell subtype[28].
Table 1 shows the typical immunohistochemical and histochemical stains for the diagnosis of lung carcinoma[29–31].
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of lung cancer, based on initial investigations, is contingent upon the presentation and observed findings[24]. Common differentials include a range of pulmonary conditions, such as bacterial, viral or fungal pneumonia, bronchitis, pleural effusion, pneumothorax and tuberculosis; however, weight loss and a suspicious CT image, combined with a positive biopsy, will distinguish from the other differentials, which are mainly infective and may occur simultaneously as lung cancer[24,32].
Staging
Staging — the process of determining the size of a cancerous tumour and how far it has grown — is helpful as it dictates treatment options, morbidity and survival. Lung cancer staging for NSCLC uses the ‘Tumour, Nodes and Metastasis (TNM)’ system, which is the same system as many other solid tumours (see Table 2[25,33]). Lung malignancy staging can inform decisions on appropriate treatment, surgical resection or palliative care if the malignancy is not curable[25]. The tumour category is divided into five categories — T0 to T4 — and then subdivided in further categories based upon the size, location and invasion of the surrounding structures[25,33]. The nodal category is divided into five categories — Nx to N3 — depending on which nodes the cancer has spread to. Similarly, the metastasis category is divided up into five categories — M0 to M1c — based upon the location and number of the metastasis. These categories together decide the stage. Table 3 shows the stage groupings of the TNM classification for NSCLC[33].
Small cell carcinoma was historically staged into two groups according to the Veterans Administration Lung Study Group staging system [34]. Limited stage and extensive stage are the main criteria for determining whether it is reasonably possible to irradiate the extent of the disease. However, SCLC now is staged with a TNM system, which is helpful for patients who are candidates for surgical resection[35].
Treatment for early-stage disease
Small-cell lung cancer
Surgical resection is offered to suitable patients with stage I– II (T1-2 N0, M0)[36]. The aim is to have a complete resection of the disease, known as an ‘R0 resection’[37]. If the patient is found to have nodal disease following surgery, chemotherapy is given adjuvantly (post surgery)[36]. Etoposide and cisplatin (EP) chemotherapy for four x 21-day cycles has been shown to beneficial in this patient cohort[38].
Patients who have stage I-III (cT1-4 N0-3 M0) should be offered chemotherapy and radiotherapy if not suitable for surgery. Performance status (PS) is an assessment of the impact a disease has on a patient’s daily living abilities according to a simple scale, where 0 is no impact and 4 is bedridden[39]. If the patient has good PS, between 0 and 1, they should have four cycles of EP chemotherapy combined with thoracic radiotherapy. If the patient’s PS is poorer (≥2), then the thoracic radiotherapy can be done sequentially.
The radiotherapy offered should be 45 Gray (Gy, a SI unit of radiation dose) delivered in 30 twice-daily fractions of 150 cGy (centigray; 0.01 of a gray), delivered with at least a 6-hour interfractional interval over 3 weeks; however, other schedules do exist with once daily fractions[40]. Use of modulated techniques (e.g. intensity modulated radiotherapy) over 3D conformal treatment is recommended to decrease the dose normal tissue toxicities[40].
Patients who have good fitness post chemoradiotherapy should be offered prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI), which is radiotherapy that is used target cancer cells in the brain. This is primarily because EP does not cross the blood-brain barrier[40]. Radiotherapy significantly reduces the likelihood of cranial metastases and improves overall survival. The recommended dose is 25Gy in 10 daily fractions. The case for offering prophylactic radiotherapy to patients with poorer fitness (PS≥2) is weaker[40].
Non-small cell lung cancer
Patients who have stage Ia and Ib NSCLC are usually offered surgery if the appropriate pre-surgical indicators are met [41]. An open thoracotomy or VATS access can be carried out to resect. If stage Ia, then some guidelines — such as the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s — recommend no adjuvant therapy[42]. Others — ESMO and NCCN — recommend radiotherapy or chemotherapy if an incomplete tumour resection is achieved (R1 or R2)[43,44].
Chemotherapy offered adjuvantly should be platinum based (cisplatin 75mg/m2 or carboplatin AUC5) combined with vinorelbine or gemcitabine or pemetrexed (for non-squamous) for three to four cycles[44]. Post operative radiotherapy comprises stereotactic body radiotherapy (SABR) 54 Gy in 27–30 fractions[45].
Patients who are not suitable for surgery should be offered primary radiotherapy to eradicate early-stage disease[41].
Patients who have Ib disease through to IIIb disease (T3 N2 only) and who have EGFR sensitising mutations exon 19 deletion (EX19del) or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutation should have adjuvant osimertinib (an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor [TKI] funded by the Cancer Drugs Fund in England and is approved for use in Scotland and Wales) for a maximum of three years[46–49]. If adjuvant chemotherapy has been given, then this should be prescribed when the course of osimertinib is finished.
Patients who have IIa, IIb and IIIa disease are recommended to have adjuvant chemotherapy after surgical resection[47]. Some guidelines, such as those from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, recommend chemoradiation for this group in incomplete tumour resection instead of adjuvant chemotherapy[44]. If chemoradiation is given, then the recommended chemotherapy is cisplatin based combined with vinorelbine[41]. Two to four cycles of chemoradiotherapy are advised; radiotherapy should be 60-66 Gy in 30–33 fractions[41]. Sequential chemotherapy then radiotherapy can be offered to patients who are not suitable for chemoradiation.
After adjuvant chemotherapy patients who have stage IIb to IIIb (N2 only) tumour may have atezolizumab IV 1,200mg or subcutaneously (SC) 1,875mg every 21 days or IV 1,680mg every 28 days (an immune checkpoint inhibitor, which binds to PD-L1 and reinvigorates the host T-cells to fight tumour cells[50]) for up to one year to prevent recurrence. This is approved by NICE and commissioned in Scotland and Wales[51,52].
Patients who have stage III disease that is deemed to be resectable may be offered chemoradiotherapy prior to surgery. Another approach offered to all patients who have a tumour ≥4cm or are node positive (excluding N3 patients) is three cycles of chemoimmunotherapy with nivolumab (another immune checkpoint inhibitor that targets the PD1 receptor) and platinum (cisplatin or carboplatin) with paclitaxel or pemetrexed (non-squamous histology) or vinorelbine or gemcitabine prior to surgery (neo-adjuvant therapy)[53]. This treatment is approved by NICE and is commissioned in Scotland and Wales[54,55].
However, if this neo-adjuvant chemotherapy is administered, no adjuvant atezolizumab or osimertinib can be used according to the treatment criteria from NHS England[56]. Osimertinib should be offered to stage III patients who do not have pre-surgical chemoimmunotherapy and who have the eligible mutations[42].
Figure 2 shows the immune checkpoint inhibitors approved by the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency[50].
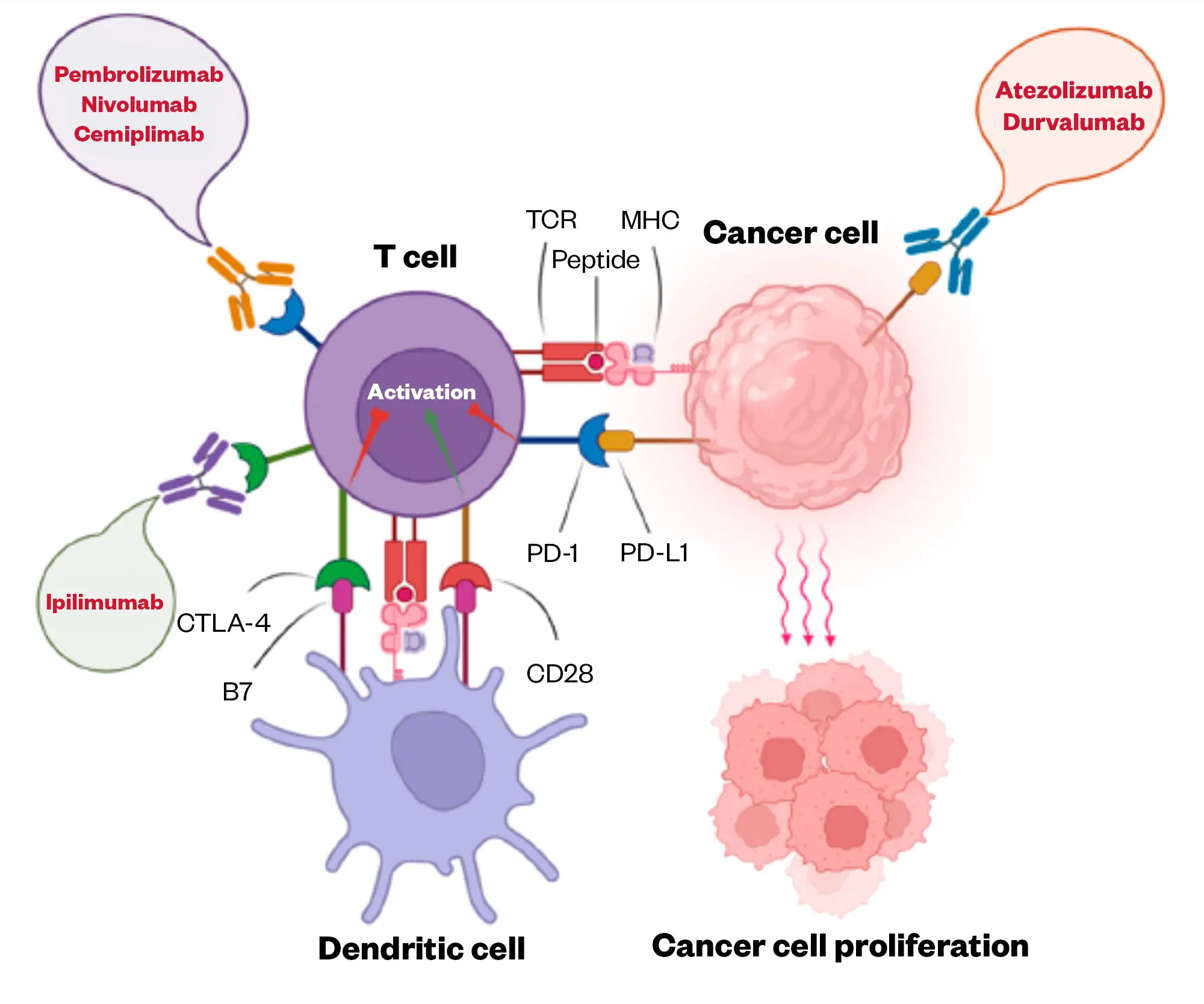
Please note that cemiplimab is licensed in the UK in the treatment of NSCLC but it is not commissioned by NHS England nor elsewhere in Great Britain.
Avelumab is not licensed in the UK for the treatment of lung cancer.
ADAPTED FROM SHIRAVAND ET AL
Patients who have stage III disease deemed not resectable should receive chemoradiation. The previously mentioned chemoradiation schedule is used[57]. After chemotherapy, patients who have not progressed should receive consolidation durvalumab IV 1,500mg every 28 days for 12 months, which is approved by NICE and is commissioned in Scotland and Wales[58,59] and trials have shown significant improvement in the median overall survival (mOS) versus patients with placebo, 47.5 months vs. 29.1 months [95% CI 0.57-0.88, HR 0.71][60].
Some research suggests that radiotherapy increases the visibility of cancer antigens, allowing the activation of T-cell response when immune checkpoint inhibitors are given[61,62].
Treatment for metastatic, advanced disease
Small-cell lung cancer
Patients who have extensive stage SCLC (i.e. non-curative stage III or stage IV) should receive four cycles of chemo-immunotherapy with atezolizumab intravenously 1,200mg for 21 days or subcutaneous 1,875mg for 21 days combined with EP chemotherapy followed by atezolizumab maintenance[56,63]. This is approved by NICE and commissioned in Wales and Scotland[64–66]. Patients need to have good fitness (PS ≤1) for this regimen.
Patients with an uncontrolled auto-immune condition are not suitable for anti-cancer immunotherapy; however, patients with a well-controlled auto-immune conditions can be switched from non-selective immunosuppressants (e.g. corticosteroids) to selective immunosuppressants (e.g. biologics, such as tocilizumab or vedolizumab in the case of inflammatory bowel disease), which is helpful in managing the risk of administering anti-cancer immunotherapy to this patient group[67]. If unsuitable for immunotherapy, then EP chemotherapy is offered. Carboplatin and gemcitabine can be used if the patient is unsuitable for EP[36].
If the patient further progresses, the timing of the relapse is important. If the patient relapses after more than three months (some guidelines state a six-month period) then this is classed as ‘platinum sensitive relapse’ and retreatment with EP is recommended. Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin and vincristine (CAV) can be used, and/or oral or IV topotecan. If the patient relapses within three to six months of finishing the first-line EP chemotherapy, this is called a ‘platinum-resistant relapse’ and retreatment with EP is not recommended[36]. There are some other treatment options for a platinum-resistant relapse, such as docetaxel, irinotecan and lurbinectedin; however, the latter is not commercially available in the UK [36].
Despite many trials, the development of new therapeutic options for relapsed advanced SCLC remains elusive[68]. In the United States, nivolumab and pembrolizumab have both been approved for patients third line, but this is not licensed in the UK[68].
A 2023 phase II trial, has shown promising results for the combination of temozolomide (a cytotoxic alkylating agent) + talazoparib (a PARP inhibitor)[68,69].
Tarlatamab is a promising therapy that targets DLL3, which is expressed in 85–94% of patients with SCLC. It is a bispecific antibody that has one core unit and two binding units that have two specific and different epitopes and can attach to two targets simultaneously. Tarlatamab is a bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) because it binds to CD3, which is present T-cells, therefore causing lysis of cancer cells. It has shown promise in a 2023 phase II study in previously treated SCLC[70]. This mechanism of action makes tarlatamab a promising therapeutic option for the treatment of SCLC[71]. BiTEs have significant adverse events, which include cytokine release syndrome and immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome; however, these adverse events are less common compared with chimeric antibody receptor T-cell therapy used currently in haematological malignancies[72].
Oncogene-addicted non-small cell lung cancer
The treatment of advanced NSCLC is determined by PDL1 expression, histology and a barrage of gene testing. The gene testing currently commissioned by NHS England for NSCLC is epidermal growth factor receptor mutations (EGFR), anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) fusion, ROS1 rearrangement, RET rearrangement, BRAF mutations, KRAS p.(G12C) mutation, MET exon 14 skipping mutations and NTRK fusions in NTRK1/2/3[73].
Advanced NSCLC management can be divided into oncogene-addicted lung cancer and non-oncogene addicted[74]. An oncogene-addicted cancer is physiologically dependent on the continued activity or overexpression of an oncogene (e.g. BRAF, ALK) to remain malignant[75]. A non-oncogene addicted malignancy does not have an instrumental oncogene. A 2019 epidemiological review demonstrated an increase in the frequency of adenocarcinoma compared with squamous lung cancers[76]. Gene mutations that are targetable occur mostly in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). The incidence of mutations in LUADs is around 10–15% but there is higher incidence in females, younger patients (aged under 60 years), those who have never smoked tobacco; and in Asian females[77].
Table 4 shows oncogene-addicted treatments for NSCLC[78–132].
Treatment following oncogene-targeted therapy
Once progression through the targeted options occurs, later treatment options include either treatment with atezolizumab, bevacizumab (an antivascular endothelial growth factor agent[133]) paclitaxel and carboplatin (ABCP) or a platinum doublet (platinum with pemetrexed preferred in non-squamous histology).
ABCP is approved by NICE and commissioned in Wales but not in Scotland[134]. In Scotland, atezolizumab is commissioned on its own directly after ALK or EGFR-targeted therapy, but in England a platinum doublet would have to have been used first[135]. Pemetrexed is a cytotoxic drug that inhibits folate metabolism and purine and pyrimidine synthesis, disrupting DNA synthesis, leading to apoptosis[136]. Once patients have progressed through this quad combination (ABCP) or the platinum doublet, docetaxel is used as second-line chemotherapy, which can be combined with nintedanib (if adenocarcinoma — NICE approved and commissioned in Wales and Scotland[137]) an inhibitor of the pathways of VEGF, fibroblast growth factor receptors and platelet-derived growth factor receptors[74].
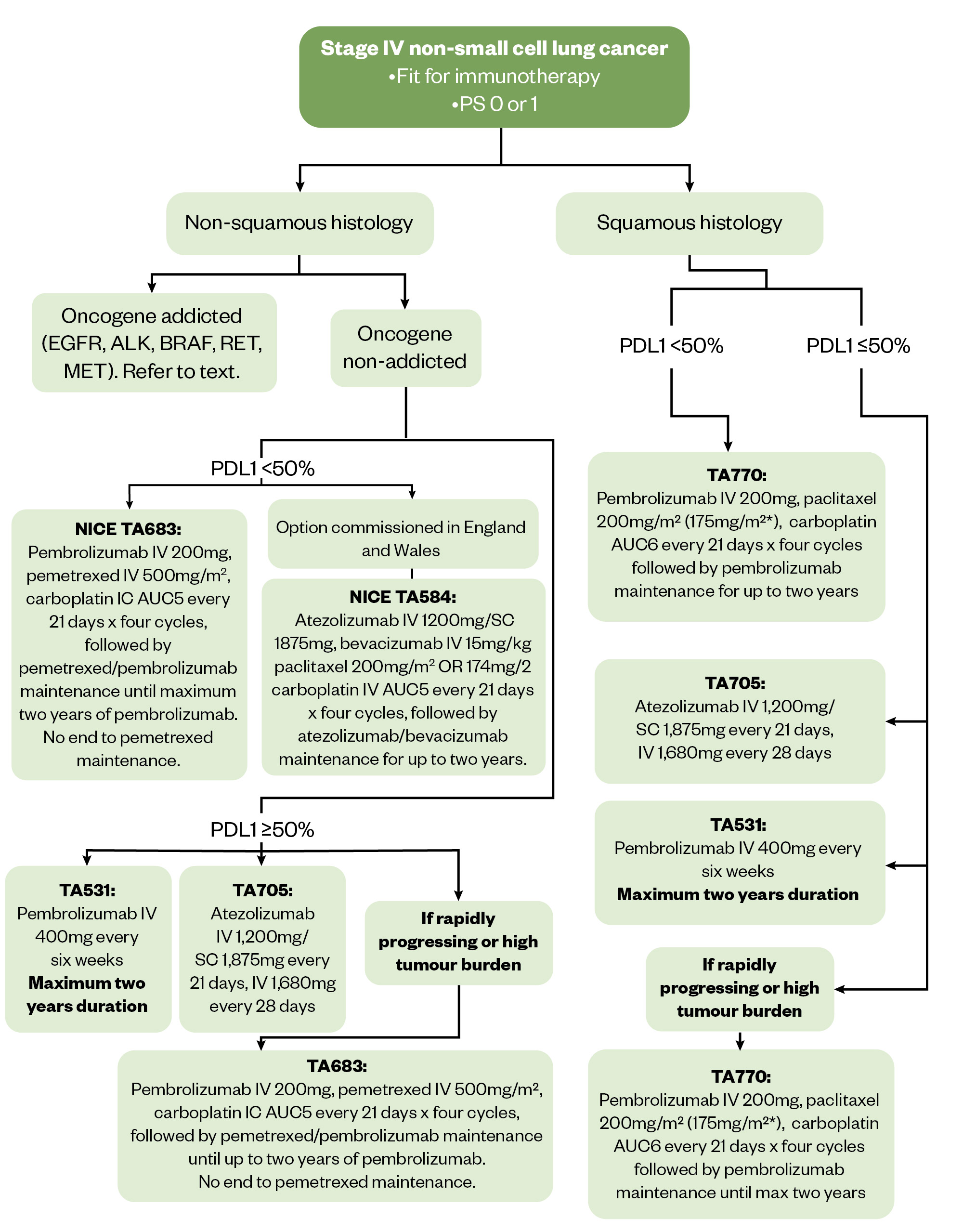
Figure 3 shows first-line treatment options for metastatic NSCLC, including the options for patients fit for immunotherapy[138]. Refer to NICE pathways for full algorithm[80].
THE PHARMACEUTICAL JOURNAL
All the NICE-approved combination treatments described in Figure 3 are commissioned in Wales. ABCP is not commissioned in in Scotland for patients who have non-squamous NSCLC with TPS <50% and no EGFR and ALK mutations.
Non-oncogene addicted non-small cell lung cancer
Non-squamous and squamous histology
The most crucial factors to consider when deciding treatment are the expression of PD-L1, the fitness to receive immunotherapy and PS. If the expression of PD-L1 is ≥50% and the patient is considered fit for ICI and has PS <2 then single agent immunotherapy with pembrolizumab (IV 200mg or 400mg, three- or six-weekly, respectively) for a maximum of two years or atezolizumab (IV 1,200mg or SC 1,875mg every three weeks/IV 1,680mg every four weeks) until progression can be offered[74]. This approach is commissioned in all parts of Great Britain[80].
There is debate about whether a single agent should be offered to patients who have expression of PD-L1 ≥50% who are fit for chemotherapy[139]. In a US Food and Drug Administation-pooled analysis in this group of patients, chemotherapy and immunotherapy were comparable in efficacy or better than immunotherapy-only treatment[140]. Clinicians offer combination therapy to patients who have rapidly progressing disease with a high tumour burden because chemotherapy can more quickly arrest the disease[141].
Following immunotherapy alone, pemetrexed + platinum (pemetrexed 500mg/m2 for non-squamous histology only and carboplatin AUC5 or cisplatin 75mg/m2 every 21 days) or another platinum doublet can be offered. Platinum doublets that are used in NSCLC include gemcitabine (IV 1,250mg/m2 day one and day eight), paclitaxel (IV 175–200mg/m2) or vinorelbine (IV 25mg/m2 or oral 60mg/m2 day one and day eight) combined with cisplatin (75–80mg/m2) or carboplatin (AUC5) every 21 days, usually for four cycles[44].
If the patient has PS 2 immunotherapy is not currently commissioned in any setting by NHS England and according to international guidelines there is a recommendation for single agent pembrolizumab/atezolizumab if PD-L1 expression is ≥50%[44,74]. A platinum doublet should be offered if PD-L1 expression is <50% as an alternative option with pemetrexed if non-squamous histology[44,74]. Best supportive care should be offered if PS is ≥3[44].
Patients who have any PD-L1 expression, are fit for chemo-immunotherapy and have a PS <2 can be treated with pembrolizumab (200mg IV three-weekly or 400mg IV six-weekly) combined with pemetrexed (if non-squamous histology) or paclitaxel (if squamous) and carboplatin chemotherapy every 21 days up to four cycles. This is commissioned by NHS England and is available in Wales; however this option in Scotland is restricted to patients who have a TPS score of <50% only. Pembrolizumab +/- pemetrexed (if non-squamous histology) maintenance are then be continued until progression or a maximum duration of two years of pembrolizumab, but the pemetrexed can continue until progression[74,142].
ABCP chemoimmunotherapy (in England and Wales) can be offered to patients with non-squamous disease with a PD-L1 expression of 0–49% up to four cycles followed by maintenance of both atezolizumab and bevacizumab until a maximum of two years including the induction cycles[44].
If for whatever reason immunotherapy is not offered initially and the patient is fit then second-line pembrolizumab (only if PD-L1>1% for maximum of two years), nivolumab (any PD-L1 expression, maximum of two years) or atezolizumab (any PD-L1 expression, maximum of two years) can be offered. All these approaches are approved by NICE[56,80].
The second-line chemotherapy option after platinum doublet chemotherapy, whether combined with immunotherapy or not, is docetaxel (IV 75mg/m2 every 21 days), which is combined with nintedanib (200mg twice daily days 2 to 21) in adenocarcinoma only[44,74].
There are limited options with efficacy following progression through docetaxel and clinical trial options should be considered or best supportive care[74].
Toxicity management
Pharmacists play a valuable role in the support of patients on anticancer medicines, by helping to address adverse events early and consequently improving pharmaceutical care[143]. They may have their own prescribing clinics where they manage their own patients and support patients with their toxicities.
Patients on chemotherapy and tyrosine kinase inhibitors
The major adverse events of the oral EGFR targeting TKIs are diarrhoea, acneiform rash and stomatitis[79]. Skin toxicities with ALK-directed therapy are rarer but gastrointestinal toxicity is most common. If these adverse events are picked up early and managed effectively then it has an impact on improving adherence to therapy[143]. There are many strategies and toxicities to the various agents used to treat lung malignancies and they are too many to outline here; however, one common example is the skin toxicities of EGFR TKIs.
The first dermatologic toxicity observed is an acneiform rash, which occurs one to two weeks after treatment. This rash can wax and wane across the course of treatment. Xerosis (dry skin) can occur owing to impairment in epidermal layer and generally occurs when patient has been treated for 30–60 days.
Paronychia can occur later in treatment, four to eight weeks after initiation and affects the big toe as its first site. Scalp lesions can also develop. It is important that the severity of the toxicities is correctly graded again the common toxicity criteria for adverse events grading because this determines the management strategy.
Figure 4 provides a general overview of the occurrence of events associated with first‐, second‐, and third‐generation EGFR‐TKIs[144].

THE PHARMACEUTICAL JOURNAL
If a grade 1 acneiform rash occurs, clindamycin 1% lotion can be prescribed, with topical corticosteroids for any possible itching[145]. For grade 2 toxicity, an oral antibiotic should be prescribed (such as doxycycline or clindamycin lotion) and a mild or moderate corticosteroid (such as clobetasone butyrate or hydrocortisone cream 1%)[145]. Usually, the SACT drug is continued if there is grade 1 or 2 toxicity. For grade 3 toxicity or greater, the SACT is suspended and all the previously mentioned strategies are employed with the addition of a short course of oral corticosteroids, such as prednisolone (0.5–1.0mg/kg daily for seven days)[143].
Patients on checkpoint inhibitors
Pharmacists have significant role to play in the monitoring of patients receiving immunotherapy, which can include the monitoring for auto-immune toxicities, such as enterocolitis, thyroid dysfunction, dermatological, hepatitis, hypoadrenalism, diabetes mellitus, myocarditis, skeletal muscle myositis, neurotoxicity and/or pneumonitis[146]. These toxicities can present acutely with diarrhoea for enterocolitis, or a skin rash for dermatological, but can also be difficult to identify without tests in the initial stages and blood tests, such as liver function and thyroid function tests, are important to identify toxicity.
More information about how pharmacists can recognise and manage these adverse events can be found in ‘Immune-related cancer toxicities: what pharmacists need to know‘[147]. The management of these toxicities once they occur may include the initiation of corticosteroids and other immunosuppressants[146].