Calyceal tumors are growths that occur in the calyces, which are parts of the kidney. Understanding these tumors can be complex, but this guide aims to simplify everything you need to know about calyceal tumors, including their pathophysiology, types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, surgeries, prevention strategies, when to see a doctor, and frequently asked questions (FAQs).
A calyceal tumor is an abnormal growth that forms in the calyces of the kidney. The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs that filter waste from the blood and produce urine. Each kidney contains several calyces that help funnel urine into the renal pelvis and ultimately into the ureter.
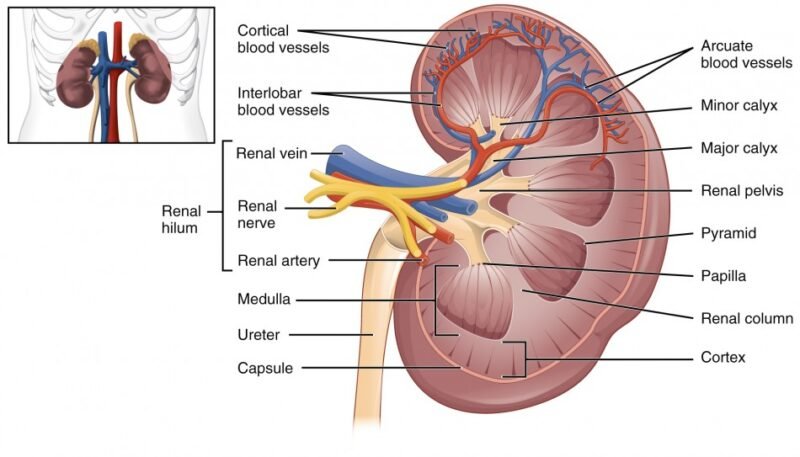
Pathophysiology of Calyceal Tumors
- Structure:
- The kidneys have an outer layer called the cortex and an inner layer called the medulla. The calyces are located in the renal pelvis and connect to the ureters.
- Tumors can affect any part of this structure, causing changes in kidney function.
- Blood Supply:
- The kidneys receive blood through the renal artery, which branches from the abdominal aorta. Blood flow is essential for kidney function and can be affected by tumors.
- Nerve Supply:
- The kidneys are innervated by the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions. This includes the regulation of blood flow and the kidney’s response to injury or disease.
Types of Calyceal Tumors
Calyceal tumors can be classified into several types based on their characteristics:
- Benign Tumors:
- Renal Adenoma: A non-cancerous growth that usually doesn’t cause symptoms.
- Angiomyolipoma: Composed of blood vessels, muscle, and fat. It is usually benign.
- Malignant Tumors:
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): The most common type of kidney cancer, which can occur in the calyces.
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma: Affects the lining of the calyces and the urinary system.
- Collecting Duct Carcinoma: A rare and aggressive form of kidney cancer.
Causes of Calyceal Tumors
There are many potential causes for calyceal tumors, including:
- Genetic Factors: Inherited conditions can increase the risk.
- Age: Older individuals are more susceptible.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is linked to several types of cancer.
- Obesity: Higher body weight increases cancer risk.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension may contribute to kidney issues.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Long-term kidney problems can lead to tumor development.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Some industrial chemicals can increase risk.
- Radiation Exposure: Previous radiation treatment can raise the risk.
- Family History of Kidney Cancer: Genetics play a role in susceptibility.
- Diabetes: This condition may contribute to kidney-related tumors.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormone imbalances may influence tumor growth.
- Cystic Kidney Diseases: Conditions like polycystic kidney disease can lead to tumors.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Chronic infections can potentially contribute to tumor formation.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups may have a higher risk.
- High Fat Diet: Diets high in saturated fats may increase cancer risk.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyle can contribute to obesity and cancer risk.
- Previous Cancer History: Individuals with a history of cancer may be at higher risk.
- Environmental Factors: Pollutants in the environment can be a risk factor.
- Chronic Inflammation: Long-term inflammation in the kidney can lead to tumors.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Certain autoimmune conditions may increase cancer risk.
Symptoms of Calyceal Tumors
Symptoms of calyceal tumors may vary but commonly include:
- Hematuria: Blood in urine, which can appear pink or red.
- Flank Pain: Pain in the side, often severe.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss may occur.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired.
- Fever: Persistent fever without an obvious cause.
- Night Sweats: Excessive sweating during the night.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Digestive issues may arise.
- Loss of Appetite: Decreased interest in eating.
- Swelling in the Abdomen: Possible abdominal mass or swelling.
- High Blood Pressure: Elevated blood pressure readings.
- Anemia: Low red blood cell count may occur.
- Difficulty Breathing: In advanced cases, respiratory problems can arise.
- Painful Urination: Discomfort while urinating.
- Increased Urination Frequency: More frequent need to urinate.
- Itching Skin: Generalized itching may occur.
- Weakness: Generalized weakness or malaise.
- Bone Pain: If the cancer has spread to bones.
- Skin Changes: Changes in skin color or texture.
- Abnormal Kidney Function Tests: Tests may indicate kidney issues.
- Hormonal Changes: Changes in hormone levels may lead to various symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests for Calyceal Tumors
Doctors may use various diagnostic tests to identify calyceal tumors, including:
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs of tumors or kidney issues.
- Blood Tests: Checking for kidney function and overall health.
- Urine Tests: Analyzing urine for blood or other abnormalities.
- Imaging Tests:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the kidneys.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the kidneys and surrounding tissues.
- MRI: Uses magnetic fields to create detailed images.
- X-rays: Can be used to check for abnormalities.
- Biopsy: Taking a sample of kidney tissue for analysis.
- Renal Angiography: Imaging blood vessels in the kidney.
- PET Scan: Uses radioactive materials to show metabolic activity in tissues.
- Kidney Function Tests: Measuring how well the kidneys filter waste.
- Bone Scans: To check if cancer has spread to bones.
- Endoscopy: Using a scope to view the urinary tract.
- CT Urography: Specialized CT scan for the urinary system.
- Serum Creatinine Test: Measures kidney function.
- Urinary Cytology: Examining urine cells for cancer.
- Genetic Testing: To identify hereditary factors.
Non-Pharmacological Treatments
Here are some non-drug treatments for managing calyceal tumors:
- Dietary Changes: A healthy diet can support overall health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve health and well-being.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water supports kidney function.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation can reduce stress.
- Physical Therapy: To help with pain management.
- Acupuncture: May help alleviate some symptoms.
- Massage Therapy: Can promote relaxation and pain relief.
- Yoga: Helps in stress reduction and improves physical fitness.
- Nutritional Supplements: Under doctor supervision, some supplements may help.
- Mindfulness Techniques: Practices like mindfulness meditation.
- Counseling: Psychological support for coping with cancer.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges.
- Palliative Care: Focuses on improving quality of life.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Changes to support overall health.
- Alternative Therapies: Such as herbal remedies (consult with a doctor).
- Homeopathy: Some individuals explore this as an adjunct therapy.
- Aromatherapy: May promote relaxation.
- Energy Healing: Practices like Reiki may help some patients.
- Chiropractic Care: For managing pain and discomfort.
- Healthy Sleep Habits: Ensuring restful sleep is crucial for recovery.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Tobacco: Limiting these substances can improve health.
- Education: Learning about the condition empowers patients.
- Routine Check-ups: Regular health check-ups for monitoring.
- Herbal Remedies: Some may provide symptom relief (under guidance).
- Spiritual Support: Engaging in spiritual practices may help.
Medications for Calyceal Tumors
Certain medications may be used to manage calyceal tumors or their symptoms, including:
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen.
- NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for pain and inflammation.
- Chemotherapy: For malignant tumors, specific drugs may be prescribed.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Helps the immune system fight cancer.
- Hormonal Therapy: For hormone-sensitive tumors.
- Antibiotics: To treat infections if they occur.
- Antidepressants: To manage anxiety or depression.
- Antiemetics: For nausea related to treatment.
- Blood Pressure Medications: To manage hypertension.
- Diuretics: To help reduce fluid retention.
- Anticoagulants: To prevent blood clots.
- Vitamin D: May support overall health.
- Pain Management Medications: Opioids for severe pain.
- Antipyretics: For fever management.
- Biphosphonates: For bone health if cancer has spread.
- Stimulants: To help with fatigue or lethargy.
- Anticonvulsants: For nerve pain management.
- Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation.
- Nutritional Support: Supplements to maintain health.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery may be necessary for calyceal tumors, depending on their type and stage:
- Partial Nephrectomy: Removing the tumor while preserving kidney function.
- Radical Nephrectomy: Removing the entire kidney and surrounding tissue.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery for tumor removal.
- Robotic Surgery: Advanced technique using robotic assistance.
- Cryoablation: Freezing the tumor to kill cancer cells.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Using heat to destroy tumor tissue.
- Transurethral Resection: Removing tumors through the urethra.
- Nephroureterectomy: Removing the kidney and ureter.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery: Targeted radiation treatment for tumors.
- Palliative Surgery: To relieve symptoms in advanced cases.
Prevention of Calyceal Tumors
While not all calyceal tumors can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can help reduce risk:
- Quit Smoking: Stop using tobacco products.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
- Manage Blood Pressure: Keep blood pressure within a healthy range.
- Control Diabetes: Effectively manage blood sugar levels.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water daily.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Drink in moderation, if at all.
- Protect Against Environmental Toxins: Avoid exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Get routine screenings and exams.
- Family History Awareness: Be aware of genetic predispositions.
- Manage Stress: Use stress reduction techniques.
- Avoid Excessive Sun Exposure: Protect skin from UV radiation.
- Follow Occupational Safety Guidelines: Protect against workplace hazards.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about risk factors.
- Stay Active: Engage in regular physical activities.
- Healthy Sleep Patterns: Aim for quality sleep.
- Monitor Kidney Health: Regular kidney function tests.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce intake of unhealthy processed foods.
- Seek Support: Engage with community and support groups.
When to See a Doctor
It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
- Blood in urine (hematuria).
- Persistent flank pain or abdominal pain.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Chronic fatigue or weakness.
- Persistent fever or night sweats.
- Difficulty urinating or painful urination.
- Swelling in the abdomen or legs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the first signs of a calyceal tumor?
- The first signs often include blood in urine and flank pain.
- Are calyceal tumors common?
- They are not the most common tumors, but renal cell carcinoma is a prevalent type of kidney cancer.
- Can calyceal tumors be benign?
- Yes, some calyceal tumors, like renal adenomas, can be benign.
- How are calyceal tumors diagnosed?
- Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests, blood tests, and sometimes a biopsy.
- What treatments are available for calyceal tumors?
- Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and non-pharmacological treatments.
- Is surgery always necessary?
- Not always; some benign tumors may only require monitoring.
- What is the survival rate for kidney cancer?
- Survival rates vary based on the stage and type of cancer. Early detection usually improves outcomes.
- Can lifestyle changes prevent calyceal tumors?
- Yes, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk.
- What types of doctors treat calyceal tumors?
- Urologists and oncologists are primarily involved in diagnosis and treatment.
- Are there any clinical trials for calyceal tumors?
- Yes, clinical trials are ongoing to test new treatments.
- How often should I get kidney screenings?
- Discuss with your doctor, especially if you have risk factors.
- What can I do for pain management?
- Pain can be managed with medications, physical therapy, and alternative therapies.
- What dietary changes should I consider?
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Can stress affect my kidney health?
- Chronic stress may negatively impact overall health, including kidney function.
- What should I do if I have a family history of kidney cancer?
- Discuss your risk with a healthcare provider and consider regular screenings.
In conclusion, understanding calyceal tumors is essential for early detection and effective management. By recognizing symptoms, knowing when to seek medical attention, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, individuals can take proactive steps in managing their kidney health. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options.
Disclaimer: Each person’s journey is unique, treatment plan, life style, food habit, hormonal condition, immune system, chronic disease condition, geological location, weather and previous medical history is also unique. So always seek the best advice from a qualified medical professional or health care provider before trying any treatments to ensure to find out the best plan for you. This guide is for general information and educational purposes only. Regular check-ups and awareness can help to manage and prevent complications associated with these diseases conditions. If you or someone are suffering from this disease condition bookmark this website or share with someone who might find it useful! Boost your knowledge and stay ahead in your health journey. We always try to ensure that the content is regularly updated to reflect the latest medical research and treatment options. Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the article.






