Galeazzi Fractures most commonly result from a fall onto an outstretched hand with an extended wrist and hyperpronated forearm. The energy from the radius fracture gets transmitted towards the radioulnar joint leading to dislocation of the DRUJ. These fractures occur with a bimodal distribution, diaphyseal forearm fractures in young males are commonly due to high-energy trauma (e.g., sports injuries, falls from height, motor vehicle collisions) and fractures in aging females are due to low-energy traumas such as falls from ground level.[rx][rx][rx]
Classification System of Galeazzi Fractures
Two classification systems have been proposed when categorizing Galeazzi fractures.
The first classifications were based on the position of the distal radius:
Type I: Dorsal displacement
Type II: Volar displacement
The second classification system is based on Rettig ME and Raskin KB who categorized Galeazzi fractures based on fracture stability. They found stability to be dependent on the distance of the radial fracture from the distal radial articular surface:
Type I:
-
Fracture occurring distally from the 7.5 cm demarcation (i.e., closer to the wrist)
-
Associated with significant DRUJ instability in more than 50% of cases
Type II:
-
Fracture occurring proximally from the 7.5 cm demarcation (i.e., further from the wrist)
-
Associated with significant DRUJ instability in only around 5% of cases
Causes of Galeazzi Fractures

- Sudden forceful fall down
- Road traffic accident
- Falls – Falling onto an outstretched hand is one of the most common causes of a broken distal radius.
- Sports injuries – Many distal radius fractures occur during contact sports or sports in which you might fall onto an outstretched hand — such as in-line skating or snowboarding.
- Motor vehicle crashes – Motor vehicle crashes can cause wrist bones to break, sometimes into many pieces, and often require surgical repair.
- Have osteoporosis – a disease that weakens your bones
- Eave low muscle mass or poor muscle strength – or lack agility and have poor balance (these conditions make you more likely to fall)
- Walk or do other activities in the snow or on the ice – or do activities that require a lot of forwarding momenta, such as in-line skating and skiing
- Wave an inadequate intake of calcium or vitamin D
- Football or soccer, especially on artificial turf
- Rugby
- Horseback riding
- Hockey
- Skiing
- Snowboarding
- In-line skating
- Jumping on a trampoline
Symptoms Of Galeazzi Fractures
Common symptoms of a distal radius fractures include:
- Severe pain that might worsen when gripping or squeezing or moving your hand or wrist
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Bruising
- Obvious deformity, such as a bent wrist
- Pain
- Bruising
- Tenderness
- The wrist hanging in a deformed way
- Pain, especially when flexing the wrist
- Deformity of the wrist, causing it to look crooked and bent.
- Your wrist is in great pain.
- Your wrist, arm, or hand is numb.
- Your fingers are pale.
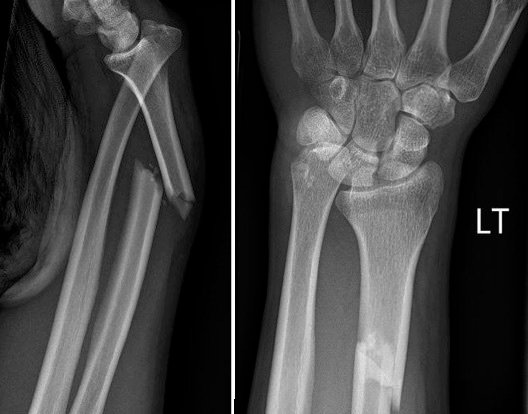
Diagnosis of Galeazzi Fractures
History
Your doctor in the emergency department may ask the following questions
-
How – How was the fracture created, and, if chronic, why is it still open? (underlying etiology)
-
When – How long has this fracture been present? (e.g., chronic less than 1 month or acute, more than 6 months)
- Where – Where on the body parts is it located? Is it in an area that is difficult to offload, complicated, or keep clean? Is it in an area of high skin tension? Is it near any vital organ and structures such as a major artery?
- What is your Past – Has your previous medical history of fracture? Are you suffering from any chronic disease, such as hypertension, blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, previous major surgery? What kind of medicine did you take? What is your food habits, geographic location, Alcohol, tea, coffee consumption habit, anabolic steroid uses for athletes, etc?
Physical
Physical examination is done by your doctor, consisting of palpation of the fracture site, eliciting boney tenderness, edema, swelling. If the fracture is in the dept of a joint, the joint motion, normal movement will aggravate the pain.
- Inspection – Your doctor also check superficial tissue, skin color, involving or not only the epidermal layer or Partial-thickness affects the epidermis and extend into the dermis, but full-thickness also extends through the dermis and into the adipose tissues or full-thickness extends through the dermis, and adipose exposes muscle, bone, evaluate and measure the depth, length, and width of the fracture. Access surrounding skin tissue, fracture margins for tunneling, rolled, undermining fibrotic changes, and if unattached and evaluate for signs and symptoms of infect warm, pain, delayed healing.
- Palpation – Physical examination may reveal tenderness to palpation, swelling, edema, tenderness, worm, temperature, open fracture, closed fracture, microtrauma, and ecchymosis at the site of fracture.
- Motor function – Your doctor may ask the patient to move the injured area to assist in assessing muscle, ligament, and tendon function. The ability to move the joint means only that the muscles and tendons work properly, and does not guarantee bone integrity or stability. The concept that “it can’t be fractured because you can move it” is not correct. The jerk test and manual test are also performed to investigate the motor function.
- Sensory examination – assesses sensations such as light touch, worm, paresthesia, itching, numbness, and pinprick sensations, in its fracture side.
- Range of motion – A range of motion examination of the fracture associate joint and it’s surrounding joint may be helpful in assessing the muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage stability. Active assisted, actively resisted exercises are performed around the injured area joint.
- Blood pressure and pulse check – Blood pressure is the term used to describe the strength of blood with which your blood pushes on the sides of your arteries as it’s pumped around your body. An examination of the circulatory system, feeling for pulses, blood pressure, and assessing how quickly blood returns to the tip of a toe to heart and it is pressed the toe turns white (capillary refill).
Lab Test
Laboratory tests should be done as an adjunct in overall medical status for surgical treatment.
- CBC, ESR test
- Random blood sugar, glucose, and routine diabetes test if the patient has diabetes mellitus.
- Microscopic urine examination test, and stool test.
- ECG, EKG test for heart abnormality is present
- Ultrasonography test in some cases.
- Normalized hemoglobin, hematocrit test
- Coagulation profile with bleeding time and coagulation time test, prothrombin time (PT) test for surgery if needed,
- Partial thromboplastin time (PTT), and platelet counts will be needed for operative intervention.
- Serum creatinine test,
- Serum lipid profile
- Serum uric acid test
Imaging
If a forearm fracture and dislocation are suspected, radiographs are warranted. An anteroposterior and lateral view will usually identify the injury. An additional oblique view may help better classify the injury. Additional radiographs of the distal wrist and proximal elbow should be obtained with any suspicion of coexistent injury.
If a distal to mid-shaft radial fracture is seen on the radiograph, a close examination of the DRUJ is merited. Signs of DRUJ disruption include:
-
Widening of the DRUJ on the PA view
-
Ulnar styloid fracture
-
Displacement of the ulna dorsally on the lateral view
-
Radial shortening greater than 5 mm (would need to compare with unaffected limb)
Usually, advanced imaging is not needed for an initial assessment. For pre-operative planning, a CT scan may be used to evaluate for non-union, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help evaluate for TFCC tears and interosseous membrane disruption.
Treatment / Management of Galeazzi Fractures
All suspected or confirmed Galeazzi fractures will require orthopedist consultation. While awaiting consult, patients should be placed in a sugar-tong splint. In most cases, conservative management is indicated in children while surgical intervention is warranted in adults. Prior reports suggested treatment with closed reduction and immobilization alone, in adults, yielded poor outcomes in greater than 90% of patients.[rx][rx]
Initial Management
Initial management for a presumed fracture includes rest, ice, immobilization, and elevation. In most cases, closed reduction of the radius followed by a reduction of the ulna in the DRUJ should be attempted in the acute setting.
Pediatrics
Children tend to have overall better long-term outcomes compared to adults. The approach is usually conservative with closed reduction and splinting. Above-elbow casting in supination is the preferred immobilization. Irreducible and unstable injuries, as well as variants of the Galeazzi fracture, may require surgical intervention with open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF).
Non-Surgical
Treatment available can be broadly
- Get medical help immediately – If you fall on an outstretched arm, get into a car accident or are hit while playing a sport and feel intense pain in your shoulder area, then get medical care immediately. Distal radius fractures cause significant pain in the front part of your shoulder, closer to the base of your neck. You’ll innately know that something is seriously wrong because you won’t be able to lift your arm up. Other symptoms include immediate swelling and/or bruising near the fracture, grinding sounds with arm movements and potential numbness and tingling in the arm/hand.
-
Apply ice to your fractured clavicle – After you get home from the hospital distal radius fractures (regardless if you had surgery or not), you should apply a bag of crushed ice (or something cold) to your injured in order to reduce the swelling and numb the pain. Ice therapy is effective for acute (recent) injuries that involve swelling because it reduces blood flow by constricting local blood vessels. Apply the crushed ice to your clavicle for 15 minutes three to five times daily until the soreness and inflammation eventually fades awayLightly exercise after the pain fades – After a couple of weeks when the swelling has subsided and the pain has faded away, remove your arm sling for short periods and carefully move your arm and shoulder in all different directions. Don’t aggravate the distal radius fractures so that it hurts, but gently reintroduce movements to the involved joints and muscles. Start cautiously, maybe starting with light calisthenics and then progress to holding light weights (five-pound weights to start). Your distal radius fractures need to move a little bit during the later phases of the injury to stimulate complete recovery.
- Practice stretching and strengthening exercises – of the fingers, elbow, and shoulder if your doctor recommends them.
- A splint – which you might use for a few days to a week while the swelling goes down; if a splint is used initially, a cast is usually put on about a week later.
- A cast – which you might need for six to eight weeks or longer, depending on how bad the break is (you might need a second cast if the first one gets too loose after the swelling goes away.)
- Get a supportive arm sling – Due to their anatomical position, distal radius fractures can’t be cast like a broken limb can. Instead, a supportive arm sling or “figure-eight” splint is typically used for support and comfort, either immediately after the injury if it’s just a hairline fracture or following surgery, if it’s a complicated fracture. A figure-eight splint wraps around both shoulders and the base of your neck in order to support the injured shoulder and keep it positioned up and back. Sometimes a larger swath of material is wrapped around the sling to keep it closer to your body. You’ll need to wear the sling constantly until there is no pain with arm movements, which takes between two to four weeks for children or four to eight weeks for adults.
- Get a referral to physical therapy – Once you’ve recovered and able to remove your arm sling splint for good, you’ll likely notice that the muscles surrounding your shoulder and upper chest look smaller and feel weaker. That’s because muscle tissue atrophies without movement. If this occurs, then you’ll need to get a referral for some physical rehabilitation. Rehab can start once you are cleared by your orthopedist, are pain-free, and can perform all the basic arm and shoulder movements. A physiotherapist or athletic trainer can show you specific rehabilitation exercises and stretches to restore your muscle strength, joint movements, and flexibility
-
Rigid fixation – osteosynthesis with locking plate, hook plate fixation, fixation with a distal radius locking plate, coracoclavicular screws, Knowles pin fixation.
-
Flexible fixation – simple k wire fixation, tension band wiring, suture anchors, vicryl tape, dacron arterial graft for coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction.
- A splint – which you might use for a few days to a week while the swelling goes down; if a splint is used initially, a cast is usually put on about a week later.
- A cast – which you might need for six to eight weeks or longer, depending on how bad the break is (you might need a second cast if the first one gets too loose after the swelling goes away.)
Rest Your Hand
- Depending on what you do for a living and if the injury is to your dominant side, you may need to take a couple of weeks off work to recuperate.
- Healing takes between four to six weeks in younger people and up to 12 weeks in the elderly, but it depends on the severity of the fractured clavicle.
- Athletes in good health are typically able to resume their sporting activities within two months of breaking they’re ulnar styloid depending on the severity of the break and the specific sport.
- Sleeping on your back (with the sling on) is necessary to keep the pressure off your shoulder and prevent stressing the clavicle injury.
Physical Therapy
- Although there will be some pain, it is important to maintain arm motion to prevent stiffness. Often, patients will begin doing exercises for elbow motion immediately after the injury. After a proximal ulna fracture, it is common to lose some shoulder and arm strength. Once the bone begins to heal, your pain will decrease and your doctor may start gentle shoulder exercises. These exercises will help prevent stiffness and weakness. More strenuous exercises will be started gradually once the fracture is completely healed.
Follow-Up Care
- You will need to see your doctor regularly until your fracture heals. During these visits, he or will take x-rays to make sure the bone is healing in a good position. After the bone has healed, you will be able to gradually return to your normal activities.
Breathing Exercise
- To elevate breathing problems or remove the lung congestion if needed.
Do no HARM for 72 hours after injury
- Heat – Heat applied to fracture and injured side by hot baths, electric heat, saunas, heat packs, etc has the opposite effect on the blood flow. Heat may cause more fluid accumulation in the fracture joints by encouraging blood flow. Heat should be avoided when inflammation is developing in the acute stage. However, after about 72 hours, no further inflammation is likely to develop and heat can be soothing.
- Alcohol – stimulates the central nervous system that can increase bleeding and swelling and decrease healing.
- Running and movement – Running and walking may cause further damage, and causes healing delay.
- Massage – A massage also may increase bleeding and swelling. However, after 72 hours of your fracture, you can take a simple message, and applying heat may be soothing the pain.
Medication
The following medications may be considered by your doctor to relieve acute and immediate pain, long term treatment
- Antibiotic – Cefuroxime or Azithromycin, or Flucloxacillin or any other cephalosporin/quinolone, meropenem antibiotic must be used to prevent infection or clotted blood removal to prevent further swelling, inflammation, and edema.
- NSAIDs – Prescription-strength drugs that reduce both pain and inflammation. Pain medicines and anti-inflammatory drugs help to relieve pain and stiffness, allowing for increased mobility and exercise. There are many common over-the-counter medicines called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They include first choice NSAIDs is Ketorolac, then Etoricoxib, then Aceclofenac, naproxen. As you are taking pain medication or NSAIDs, your doctor must prescribe a standard anti-ulcer drug, such as omeprazole, pantoprazole, esomeprazole, dexlansoprazole, etc.
- Muscle Relaxants – These medications provide relief from spinal muscle spasms, spasticity. Muscle relaxants, such as baclofen, tolperisone, eperisone, methocarbamol, carisoprodol, and cyclobenzaprine, may be prescribed to control postoperative muscle spasms, spasticity, stiffness, contracture.
- Calcium & vitamin D3 – To improve bone health, blood clotting, helping muscles to contract, regulating heart rhythms, nerve functions, and healing fractures. As a general rule, too absorbed more minerals for men and women age 50 and older should consume 1,200 milligrams of calcium a day, and 600 international units of vitamin D a day to heal back pain, fractures, osteoarthritis.
- Neuropathic Agents – Drugs(pregabalin & gabapentin) that address neuropathic—or nerve-related—pain. This includes burning, numbness, tingling sensation, and paresthesia.
- Glucosamine & Diacerein, Chondroitin sulfate – can be used to tighten the loose tendon, cartilage, ligament, and cartilage, ligament regenerates cartilage or inhabits the further degeneration of cartilage, ligament. The dosage of glucosamine is 15oo mg per day in divided dosage and chondroitin sulfate approximately 500mg per day in different dosages, and diacerein minimum of 50 mg per day may be taken if the patient suffers from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and any degenerative joint disease.[rx]
- Topical Medications and essential oil – These prescription-strength creams, gels, ointments, patches, and sprays help relieve pain and inflammation in acute trauma, pain, swelling, tenderness through the skin. If the fracture is closed and not open fracture then you can use this item.
- Antidepressants – A drug that blocks pain messages from your brain and boosts the effects of endorphins in your body’s natural painkillers. It also helps in neuropathic pain, anxiety, tension, and proper sleep.
- Corticosteroids – Also known as oral steroids, these medications reduce inflammation. To heal the nerve inflammation and clotted blood in the joints.
- Dietary supplement – To eradicate the healing process from fracture your body needs a huge amount of vitamin C, and vitamin E. From your dietary supplement, you can get it, and also need to remove general weaknesses & improved health.
- Cough Syrup – If your doctor finds any chest congestion or fracture-related injury in your chest, dyspnoea, post-surgical breathing problem, then advice you to take bronchodilator cough syrup.
What To Eat and What to avoid
Eat Nutritiously During Your Recovery
All bones and tissues in the body need certain micronutrients in order to heal properly and in a timely manner. Eating a nutritious and balanced diet that includes lots of minerals and vitamins is proven to help heal broken bones and all types of fractures. Therefore, focus on eating lots of fresh food produce (fruits and veggies), whole grains, cereal, beans, lean meats, seafood, and fish to give your body the building blocks needed to properly repair your fracture. In addition, drink plenty of purified mineral water, milk, and other dairy-based beverages to augment what you eat.
- Broken bones or fractures bones need ample minerals (calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, boron, selenium, omega-3) and protein to become strong and healthy again.
- Excellent sources of minerals/protein include dairy products, tofu, beans, broccoli, nuts and seeds, sardines, sea fish, and salmon.
- Important vitamins that are needed for bone healing include vitamin C (needed to make collagen that your body essential element), vitamin D (crucial for mineral absorption, or machine for mineral absorber from your food), and vitamin K (binds calcium to bones and triggers more quickly collagen formation).
- Conversely, don’t consume food or drink that is known to impair bone/tissue healing, such as alcoholic beverages, sodas, fried fast food, most fast food items, and foods made with lots of refined sugars and preservatives.