The head and neck region is one of the most complex anatomical areas in the human body, housing a multitude of structures that serve essential functions in protection, communication, sensory perception, and overall coordination of bodily activities. Understanding the anatomy of this region is crucial not only for medical professionals but also for anyone interested in the intricate design and function of the human body. This overview delves into the skeletal framework, muscular components, nervous and vascular systems, and the key sensory organs that reside in the head and neck.
Skeletal Framework
The skeletal structure of the head is primarily composed of two major components: the cranium and the facial bones. The cranium is a rigid, bony structure that encases and protects the brain. It consists of several bones fused together by immovable sutures, including the frontal bone (forehead), parietal bones (sides and roof), occipital bone (back of the skull), temporal bones (sides, housing the structures of the ear), sphenoid bone (forming the base of the skull and part of the eye socket), and the ethmoid bone (contributing to the nasal cavity and eye orbits). Together, these bones form a secure and protective box around the brain, ensuring that it is safeguarded from physical impacts.
The facial skeleton comprises bones that give shape to the face and support the functions of eating, breathing, and expression. Notable facial bones include the maxillae (upper jaw), mandible (lower jaw), nasal bones, zygomatic bones (cheekbones), lacrimal bones, and palatine bones, among others. The mandible is particularly important as it not only forms the lower facial contour but also plays a critical role in mastication (chewing) and speech.
Moving to the neck, the vertebral column begins with the cervical spine, which is composed of seven cervical vertebrae. These vertebrae are smaller and more mobile compared to those in the thoracic or lumbar regions, allowing for a wide range of head movements. The first cervical vertebra, known as the atlas, supports the skull, while the second vertebra, the axis, provides a pivot point that allows for rotational movement of the head. The cervical spine also protects the upper part of the spinal cord, which is responsible for transmitting nerve signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Muscular System
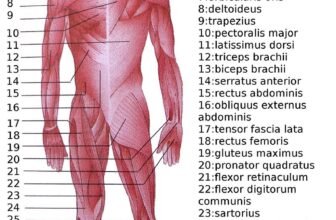
Muscles in the head and neck region are responsible for an array of functions, from facial expressions and mastication to head movement and swallowing. In the head, the muscles of facial expression are vital for non-verbal communication. These muscles, such as the orbicularis oculi (around the eyes), orbicularis oris (around the mouth), and zygomaticus muscles (extending from the cheekbones), enable subtle facial movements that convey emotion and intent.
The muscles of mastication include the masseter, temporalis, and the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles. These muscles work together to facilitate chewing, grinding food, and controlling the movement of the mandible. Their coordinated action is essential for proper digestion and nutrition.
The neck houses several important muscle groups that contribute to both movement and support. The sternocleidomastoid is one of the most prominent neck muscles, running from the sternum and clavicle to the mastoid process of the skull. It plays a key role in rotating and flexing the head. The trapezius, a broad muscle extending from the occipital bone to the mid-back, assists in moving and stabilizing the scapulae and supports head movement. Other smaller muscles in the neck facilitate swallowing, speech, and fine motor adjustments necessary for maintaining posture and balance.
Nervous System
The head and neck are integral to the functioning of the nervous system, containing both the brain and a network of nerves that control sensory and motor functions. The brain, encased within the skull, is the command center for the entire body. It coordinates voluntary and involuntary actions, processes sensory information, and regulates cognitive functions such as memory, reasoning, and emotion.
Emerging from the brain are the cranial nerves, twelve pairs of nerves that serve various sensory and motor functions. For example, the olfactory nerve (I) is responsible for the sense of smell, while the optic nerve (II) transmits visual information from the eyes. The facial nerve (VII) controls the muscles of facial expression and conveys taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. Other cranial nerves are involved in hearing, balance, swallowing, and even parasympathetic regulation of internal organs. Their precise and coordinated function is essential for everyday activities.
In the neck, the cervical spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord and innervate various muscles and sensory regions of the upper body, neck, and upper limbs. These nerves form a complex network that ensures rapid communication between the brain and peripheral structures, allowing for coordinated movement and sensory perception.
Vascular System
The head and neck region boast an extensive vascular network that is crucial for delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products. The carotid arteries are the primary blood vessels that supply the brain with oxygenated blood. They branch into the internal and external carotid arteries, with the internal carotid artery entering the skull to provide blood to the brain, and the external carotid artery supplying the facial structures and scalp.
Complementing the arterial supply are the jugular veins, which are responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the brain, face, and neck back to the heart. Additionally, the vertebral arteries travel along the cervical spine and contribute to the blood supply of the brainstem and cerebellum. This intricate vascular system ensures that all regions of the head and neck receive a continuous and regulated blood flow.
Sensory Organs
The head is the seat of the major sensory organs that provide us with the means to experience and interpret the world around us. The eyes serve as the windows to our environment, capturing light and converting it into visual signals interpreted by the brain. The ears are essential for hearing and balance; the outer ear funnels sound waves to the middle ear, where vibrations are transmitted to the inner ear and then converted into electrical signals.
The nose is responsible for our sense of smell, detecting airborne chemicals and playing a significant role in taste perception. Finally, the tongue is not only critical for tasting and chewing but also for articulating speech. Together, these organs form the core of our sensory system, enabling us to perceive and interact with our surroundings.
Lymphatic System and Other Structures
In addition to the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and vascular systems, the head and neck contain a well-developed lymphatic network that plays a key role in immune surveillance and fluid balance. Lymph nodes are scattered throughout this region, particularly along the neck, where they filter lymphatic fluid and help defend against infections and other foreign substances.
Other important structures include the salivary glands, which produce saliva to initiate digestion and maintain oral hygiene, and various endocrine glands such as the thyroid and parathyroid glands. The thyroid gland, located in the lower front of the neck, regulates metabolism, while the smaller parathyroid glands are critical for maintaining calcium balance in the body.
Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
- cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- galea aponeurotica
- fontanelle
- anterior fontanelle
- posterior fontanelle
- anterolateral (sphenoidal) fontanelle
- posterolateral (mastoid) fontanelle
- sutures
- calvarial
- coronal suture
- sagittal suture
- lambdoid suture
- accessory occipital bone sutures
- metopic suture
- squamosal suture
- sphenosquamosal suture
- squamomastoid suture
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- frontoethmoidal suture
- petrosquamous suture
- petroclival suture
- sphenoethmoidal suture
- sphenopetrosal suture
- calvarial
- skull landmarks
- nasion
- glabella
- bregma
- vertex
- lambda
- inion
- pterion
- asterion
- basion
- opisthion
- obelion
- frontal bone
- supratrochlear foramen
- supraorbital foramen
- temporal bone
- squamous part
- MacEwen triangle
- mandibular fossa
- sigmoid plate
- petrous part
- petrous apex
- Fallopian canal
- jugular fossa
- inferior tympanic canaliculus
- petrous ridge
- Dorello canal
- petromastoid canal
- mastoid part
- mastoid antrum
- mastoid air cells
- Koerner septum
- mastoid canaliculus
- mastoid foramen
- tympanic part
- tympanosquamous fissure
- styloid process
- stylomastoid foramen
- styloid apparatus
- stylohyoid ligament
- squamous part
- parietal bone
- parietal foramen
- occipital bone
- clivus
- inferior median clival canal
- foveola pharyngica recess
- inferior median clival canal
- occipital condyle
- bathrocephaly
- clivus
- scalp (mnemonic)
- skull base (foramina)
- anterior cranial fossa
- anterior ethmoidal foramen
- posterior ethmoidal foramen
- foramen cecum
- cribriform plate
- middle cranial fossa (mnemonic)
- foramen rotundum
- foramen ovale (mnemonic)
- foramen spinosum
- foramen Vesalii
- foramen lacerum
- carotid canal
- pterygoid canal
- posterior cranial fossa
- condylar canal
- jugular foramen
- jugular spine
- hypoglossal canal
- foramen magnum
- anterior cranial fossa
- facial bones
- midline single bones
- sphenoid bone
- body
- pituitary fossa
- sella turcica
- bridging of the sella turcica
- dorsum sellae
- pneumatized dorsum sellae
- tuberculum sellae
- sella turcica
- optic strut
- persistent hypophyseal canal
- vomerovaginal canal
- jugum sphenoideum
- pituitary fossa
- lesser wing
- greater wing
- pterygoid processes
- palatovaginal canal
- body
- ethmoid bone
- cribriform plate
- crista galli
- olfactory fossa
- Keros classification
- labyrinth of ethmoid
- lamina papyracea
- cribriform plate
- vomer
- mandible
- temporomandibular joint
- articular disc
- retrodiscal zone
- pterygoid fovea
- lingula
- sphenomandibular ligament
- stylomandibular ligament
- mandibular foramen
- mandibular canal
- mental foramen
- temporomandibular joint
- sphenoid bone
- paired bilateral bones
- maxilla
- incisive canal
- incisive foramen
- incisive canal
- palatine bone
- sphenopalatine foramen
- greater palatine foramen (canal)
- lesser palatine foramina (canal)
- nasal bone
- lacrimal bone
- zygoma (zygomatic bone)
- zygomaticofacial foramen
- zygomaticotemporal foramen
- zygomatic arch
- maxilla
- midline single bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
- arytenoid cartilage
- corniculate cartilage
- cuneiform cartilage
- cricoid cartilage
- thyroid cartilage
- cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- extrinsic muscles of the tongue
- genioglossus muscle
- hyoglossus muscle
- styloglossus muscle
- palatoglossus muscle
- intrinsic muscles of the tongue
- superior longitudinal muscle of the tongue
- inferior longitudinal muscle of the tongue
- transverse muscle of the tongue
- vertical muscle of the tongue
- extrinsic muscles of the tongue
- muscles of mastication
- temporalis muscle
- masseter muscle
- medial pterygoid muscle
- lateral pterygoid muscle
- facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- occipitofrontalis muscle
- frontalis muscle
- occipitalis muscle
- temporoparietalis muscle
- occipitofrontalis muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- orbicularis oculi muscle
- corrugator supercilii muscle
- levator palpebrae superioris muscle
- nasal muscles
- procerus muscle
- nasalis muscle
- compressor naris muscle
- dilator naris muscle
- myrtiformis muscle
- depressor septi nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
- orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
- orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- buccinator muscle
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- epicranius muscle
- muscles of the middle ear
- stapedius muscle
- tensor tympani muscle
- orbital muscles
- extraocular muscles
- superior rectus muscle
- inferior rectus muscle
- lateral rectus muscle
- medial rectus muscle
- superior oblique muscle
- inferior oblique muscle
- levator palpebrae superioris muscle
- superior tarsal muscle
- extraocular muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- tensor veli palatini muscle
- levator veli palatini muscle
- palatopharyngeus muscle
- palatoglossus muscle
- muscle of the uvula
- pharyngeal muscles
- superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
- Passavant cushion
- middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle
- inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
- Killian dehiscence
- stylopharyngeus muscle
- salpingopharyngeus muscle
- superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
- suprahyoid muscles
- digastric muscle
- geniohyoid muscle
- mylohyoid muscle
- mylohyoid boutonniere
- stylohyoid muscle
- infrahyoid muscles
- sternohyoid muscle
- sternothyroid muscle
- thyrohyoid muscle
- omohyoid muscle
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- colliscalene triangle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
- suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- levator glandulae thyroideae muscle
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- deep cervical fascia
- superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia
- middle layer of the deep cervical fascia
- pharyngobasilar fascia
- sinus of Morgagni
- pharyngobasilar fascia
- deep layer of the deep cervical fascia
- deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- carotid sheath
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- alar fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- pterygomaxillary fissure
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- anterior triangle
- digastric triangle
- carotid triangle
- muscular triangle
- submental triangle
- posterior triangle
- occipital triangle
- suboccipital triangle
- supraclavicular triangle
- occipital triangle
- anterior triangle
- orbit
- bony orbit
- anterior ethmoidal notch
- orbital apex
- optic canal
- superior orbital fissure (mnemonic)
- inferior orbital fissure
- infraorbital foramen
- tendinous ring
- supraorbital ridge
- orbital spaces
- extraconal
- myofascial cone
- intraconal
- ocular globe
- conjunctiva
- cornea
- sclera
- uvea
- iris
- ciliary body
- choroid
- ora serrata
- vitreous body
- Cloquet’s canal
- lens
- optic nerve-sheath complex
- fovea
- orbital septum
- naso-orbitoethmoid region
- eye movements
- ocular adductors
- ocular abductors
- ocular elevators
- ocular depressors
- ocular internal rotators
- ocular external rotators
- orbital blood supply
- ophthalmic artery
- superior ophthalmic vein
- inferior ophthalmic vein
- orbital nerve supply
- lacrimal apparatus
- lacrimal gland
- nasolacrimal drainage apparatus
- lacrimal canaliculi
- lacrimal sac
- nasolacrimal duct
- bony orbit
- ear
- inner ear
- internal acoustic meatus (mnemonic)
- Bill bar
- falciform crescent
- porus acusticus internus
- labyrinth
- osseous labyrinth
- cochlea
- modiolus
- spiral lamina
- helicotrema
- modiolus
- cochlear aqueduct
- semicircular canals
- vestibule
- macula cribrosa
- vestibular aqueduct
- cochlea
- perilymph
- membranous labyrinth
- cochlear duct (scala media)
- organ of Corti (Spiral organ)
- scala vestibuli
- scala tympani
- perilymphatic duct
- semicircular ducts
- saccule
- utricle
- endolymphatic duct
- cochlear duct (scala media)
- endolymph
- osseous labyrinth
- internal acoustic meatus (mnemonic)
- middle ear
- hypotympanum
- Eustachian tube
- mesotympanum
- cochlear promontory
- fissula ante fenestram
- facial recess
- pyramidal eminence
- sinus tympani
- oval window
- round window
- ossicular chain
- malleus
- incus
- stapes
- incudomalleolar joint
- incudostapedial joint
- stapediovestibular joint
- epitympanum
- anterior epitympanic recess
- Prussak space
- hypotympanum
- external ear
- external auditory meatus
- foramen tympanicum
- porus acusticus externus
- external auditory canal
- scutum
- tympanic membrane
- pars tensa
- pars flaccida
- tympanic annulus
- external auditory meatus
- inner ear
- paranasal sinuses
- frontal sinuses
- maxillary sinuses
- maxillary ostium
- accessory maxillary ostium
- ethmoid air cells (sinuses)
- ethmoidal infundibulum
- ethmoid bulla
- bulla lamella
- suprabullar recess
- retrobullar recess
- bulla lamella
- agger nasi air cells
- infraorbital ethmoidal air cells
- sphenoethmoidal air cells
- supraorbital air cells
- sphenoid sinuses
- sphenoethmoidal recess
- extramural air cell
- ostiomeatal complex
- ostiomeatal narrowing due to variant anatomy
- upper respiratory tract
- nose
- external nose
- nasal cartilages
- nasal vestibule
- anterior naris
- nasal ala
- nasal sill
- columella
- nasal septum
- pyriform aperture
- nasal cavity
- inferior meatus
- Woodruff plexus
- nasal concha
- inferior
- middle
- concha bullosa
- paradoxical middle turbinate
- hiatus semilunaris
- uncinate process
- superior
- supreme
- Kiesselbach plexus
- inferior meatus
- Schneiderian epithelium
- external nose
- oral cavity
- palate
- hard palate
- soft palate
- uvula
- floor of mouth
- retromolar trigone
- sublingual space
- submandibular space
- submental space
- tongue
- root of tongue
- teeth (dental terminology)
- supernumerary teeth
- mesiodens
- hypodontia
- supernumerary teeth
- palate
- pharynx
- nasopharynx
- Rosenmüller fossa
- torus tubarius
- oropharynx
- vallecula
- hypopharynx
- pyriform sinus (fossa)
- nasopharynx
- larynx
- supraglottic space
- aryepiglottic folds
- epiglottis
- omega epiglottis
- false vocal cords
- laryngeal ventricle
- laryngeal saccule
- laryngeal vestibule
- glottis
- subglottic space
- true vocal cords
- anterior commissure of the larynx
- true vocal cords
- supraglottic space
- nose
- viscera of the neck
- Waldeyer ring
- nasopharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
- palatine tonsils
- lingual tonsils
- thyroid gland
- pyramidal lobe of thyroid
- ectopic thyroid
- Zuckerkandl tubercle
- thyroglossal duct
- parathyroid gland
- salivary glands and ducts
- major salivary glands
- parotid gland
- parotid duct
- accessory parotid gland
- submandibular gland
- submandibular (Wharton) duct
- sublingual gland
- duct of Rivinus
- parotid gland
- minor salivary glands
- major salivary glands
- esophagus
- trachea
- Waldeyer ring
- blood supply of the head and neck
- arterial supply
- common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- internal carotid artery (segments)
- artery of Bernasconi and Cassinari
- caroticotympanic artery
- persistent stapedial artery
- ophthalmic artery
- supraorbital artery
- lacrimal artery
- central artery of the retina
- supratrochlear artery
- dorsal nasal artery
- external carotid artery (mnemonic)
- superior thyroid artery
- superior laryngeal artery
- ascending pharyngeal artery
- lingual artery
- facial artery
- inferior labial artery
- superior labial artery
- angular artery
- occipital artery
- posterior auricular artery
- (internal) maxillary artery (mnemonic)
- deep auricular artery
- middle meningeal artery
- greater (descending) palatine artery
- inferior alveolar artery
- mental artery
- sphenopalatine artery
- anterior ethmoidal artery
- posterior ethmoidal artery
- infraorbital artery
- masseteric artery
- buccinator artery
- deep temporal arteries
- Vidian artery
- superficial temporal artery
- superior thyroid artery
- internal carotid artery (segments)
- subclavian artery
- vertebral artery
- internal thoracic artery
- thyrocervical trunk
- inferior thyroid artery
- suprascapular artery
- ascending cervical artery
- transverse cervical artery
- dorsal scapular artery
- costocervical trunk
- variants
- thyroidea ima artery
- common carotid artery
- venous drainage
- internal jugular vein (mnemonic)
- jugular bulb
- asymmetrically large jugular bulb
- pharyngeal vein
- common facial vein
- angular vein
- supraorbital vein
- supratrochlear vein
- angular vein
- lingual vein
- superior thyroid vein
- middle thyroid vein
- jugular bulb
- external jugular vein (mnemonic)
- posterior auricular vein
- retromandibular vein
- superficial temporal vein
- (deep/internal) maxillary vein
- pterygoid venous plexus
- facial vein
- anterior jugular vein
- posterior external jugular vein
- suprascapular vein
- transverse cervical vein
- cavernous sinus
- facial-cavernous anastomoses
- anterior condylar confluence
- internal jugular vein (mnemonic)
- arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
- cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- tentorial nerve
- frontal nerve
- supra-orbital nerve
- supratrochlear nerve
- lacrimal nerve
- nasociliary nerve
- small communicating branch to the ciliary ganglion
- short ciliary nerves
- long ciliary nerves
- infratrochlear nerve
- posterior ethmoidal nerve
- anterior ethmoidal nerve
- maxillary division
- middle meningeal nerve
- zygomatic nerve
- zygomaticotemporal nerve
- zygomaticofacial nerve
- infra-orbital nerve
- posterior superior alveolar nerve
- middle superior alveolar nerve
- anterior superior alveolar nerve
- nasopalatine nerve
- posterior superior nasal nerves
- greater palatine nerve
- lateral posterior inferior nasal nerve
- lesser palatine nerves
- pharyngeal nerve
- mandibular division
- nervus spinosus
- nerve to medial pterygoid
- anterior division
- deep temporal nerves
- lateral pterygoid nerves
- masseteric nerve
- buccal nerve
- posterior division
- auriculotemporal nerve
- lingual nerve
- inferior alveolar nerve
- nerve to mylohyoid
- incisive nerve
- mental nerve
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
- chorda tympani
- nerve to stapedius
- vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa’s ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- Jacobson nerve
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- superior laryngeal nerve
- external laryngeal nerve
- internal laryngeal nerve
- recurrent laryngeal nerve (inferior laryngeal nerve)
- non-recurrent laryngeal nerve
- superior laryngeal nerve
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- ciliary ganglion
- pterygopalatine ganglion
- otic ganglion
- submandibular ganglion
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- superior cervical ganglion
- middle cervical ganglion
- inferior cervical ganglion
- stellate ganglion
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
- cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- scalenus anterior
- scalenus medius
- scalenus posterior
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
- ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- accessory phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- less occipital nerve
- greater auricular nerve
- transverse cervical nerve
- supraclavicular nerve
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
- cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- cervical lymph node groups
- Delphian node
- intraparotid lymph nodes
- jugular trunk
- cervical lymph node levels
- supraclavicular lymph nodes
- cervical lymph node groups
- embryological development of the head and neck
- branchial apparatus
Disclaimer: Each person’s journey is unique, treatment plan, life style, food habit, hormonal condition, immune system, chronic disease condition, geological location, weather and previous medical history is also unique. So always seek the best advice from a qualified medical professional or health care provider before trying any treatments to ensure to find out the best plan for you. This guide is for general information and educational purposes only. Regular check-ups and awareness can help to manage and prevent complications associated with these diseases conditions. If you or someone are suffering from this disease condition bookmark this website or share with someone who might find it useful! Boost your knowledge and stay ahead in your health journey. We always try to ensure that the content is regularly updated to reflect the latest medical research and treatment options. Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the article.