Brain Dermoid Cysts are rare growths that can develop in the brain. These cysts are filled with different types of tissue, such as hair, skin, and even teeth. In this article, we’ll provide plain English explanations for various aspects of Brain Dermoid Cysts, making it easy to understand.
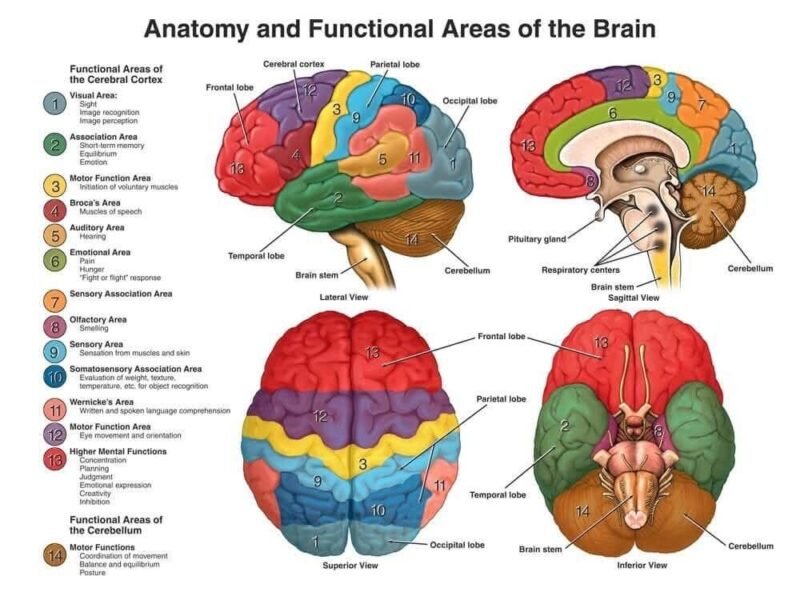
Types of Brain Dermoid Cysts:
- Epidermoid Cysts:
- These cysts form from cells on the surface of the brain.
- They contain skin cells and skin-related substances.
- Dermoid Cysts:
- These cysts contain a mix of tissues, including hair and sweat glands.
- They can be present from birth or develop later in life.
- Teratoma Cysts:
- Teratomas are more complex cysts that may contain various types of tissues, including muscle, bone, and nerve tissue.
- They are rare and may grow slowly.
Brain Dermoid Cysts come in different types, depending on their location and characteristics. Here are the main types:
- Intracranial Dermoid Cysts: These cysts develop inside the brain.
- Spinal Dermoid Cysts: These cysts form within the spinal cord or spinal canal.
- Extracranial Dermoid Cysts: These cysts grow outside the brain, often on the skin.
- Nasopharyngeal Dermoid Cysts: These cysts occur near the nasal passages.
Causes of Brain Dermoid Cysts:
- Congenital Factors:
- Some people are born with Brain Dermoid Cysts, and these may become apparent later in life.
- The exact cause of congenital Brain Dermoid Cysts is not fully understood.
- Developmental Abnormalities:
- Irregularities during fetal brain development can lead to the formation of these cysts.
- These abnormalities can include problems with cell growth and tissue development.
- Genetic Predisposition:
- In some cases, genetics may play a role, with a family history of brain cysts.
- However, this is not common and is mostly seen in rare familial cases.
Symptoms of Brain Dermoid Cysts:
- Headaches:
- Frequent, severe headaches can be a symptom, often due to increased pressure within the skull.
- Seizures:
- Brain Dermoid Cysts can irritate brain tissue, leading to seizures.
- Vision Problems:
- Depending on their location, these cysts can affect vision and lead to problems like blurred vision or double vision.
- Cognitive Changes:
- Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and confusion may occur if the cysts interfere with brain function.
- Nausea and Vomiting:
- Increased pressure on the brain can cause nausea and vomiting.
- Personality Changes:
- Some individuals may experience mood swings or personality changes as a result of cyst-related pressure on the brain.
- Weakness or Numbness:
- If the cysts press on specific brain regions, it can lead to weakness or numbness in parts of the body.
- Balance Issues:
- Coordination problems and difficulties with balance can be symptoms of Brain Dermoid Cysts.
Diagnostic Tests for Brain Dermoid Cysts:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
- This imaging test provides detailed pictures of the brain and can identify the presence and location of cysts.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography):
- CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the brain, helping to diagnose cysts.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap):
- A spinal tap can analyze cerebrospinal fluid for abnormalities associated with Brain Dermoid Cysts.
- Neurological Examination:
- A thorough evaluation by a neurologist can help detect symptoms and assess brain function.
- Biopsy (in some cases):
- A tissue sample may be collected through surgery to confirm the nature of the cyst.
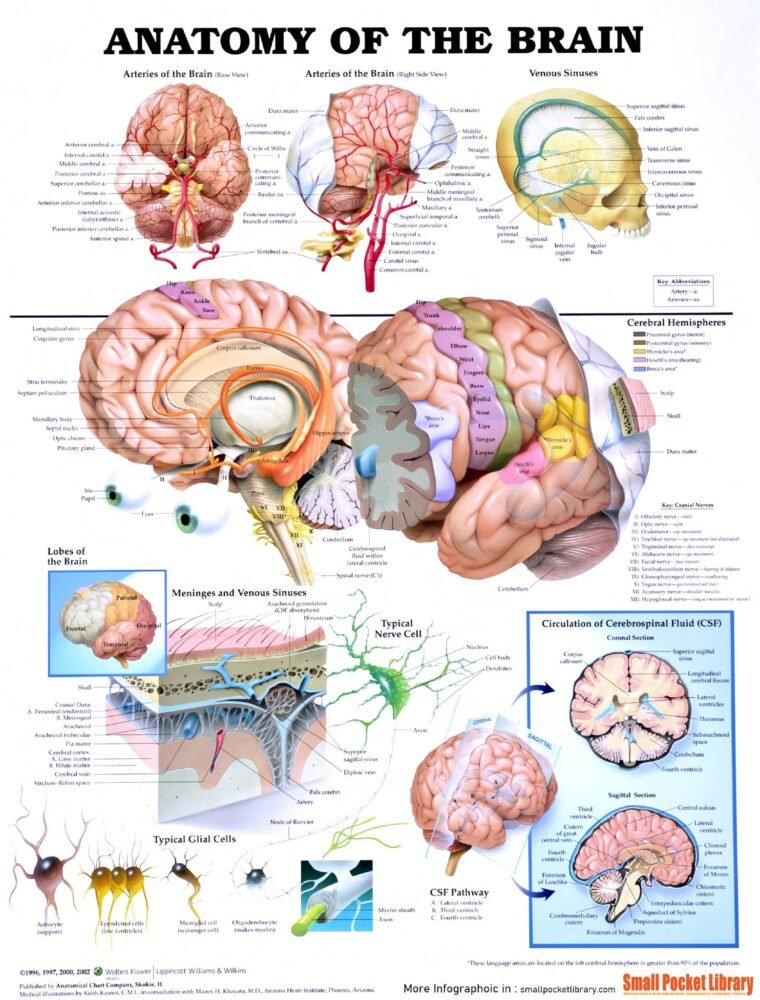
Treatment Options for Brain Dermoid Cysts:
- Observation:
- If the cyst is small and not causing significant symptoms, your doctor may recommend regular monitoring without immediate treatment.
- Medication:
- Medications can help manage symptoms like headaches and seizures.
- Surgical Removal:
- Surgery may be necessary to remove the cyst if it’s causing severe symptoms, pressing on vital brain structures, or growing rapidly.
- Shunt Placement:
- In some cases, a shunt may be inserted to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid and relieve pressure.
- Endoscopic Surgery:
- Minimally invasive endoscopic techniques can be used to remove smaller cysts through small incisions.
- Radiation Therapy (in rare cases):
- Radiation may be considered for cysts that cannot be safely removed surgically.
- Stereotactic Aspiration:
- A precise procedure where a needle is inserted to drain the cyst’s contents.
Medications for Managing Brain Dermoid Cyst Symptoms:
- Pain Relievers:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or prescribed pain medications can help with headaches.
- Antiseizure Medications:
- Drugs like carbamazepine or phenytoin can control seizures.
- Anti-nausea Medications:
- These can be prescribed to manage nausea and vomiting.
- Cognitive Enhancers:
- Medications like donepezil may help improve cognitive function.
- Steroids:
- Corticosteroids can reduce swelling and inflammation around the cyst.
Surgery for Brain Dermoid Cysts:
- Craniotomy:
- A traditional surgical approach where a section of the skull is removed to access and remove the cyst.
- Endoscopic Surgery:
- A less invasive procedure involving small incisions and a camera-guided tool to remove the cyst.
- Stereotactic Biopsy:
- A precise needle biopsy to obtain a tissue sample for diagnosis.
- Shunt Placement:
- Inserting a shunt can help relieve pressure by draining excess cerebrospinal fluid.
- Laser Ablation:
- Laser technology can be used to vaporize cyst contents and collapse the cyst walls.
Conclusion:
Brain Dermoid Cysts are rare but can cause a range of symptoms, from headaches to seizures. Proper diagnosis through imaging and neurological evaluations is crucial. Treatment options vary depending on the size, location, and symptoms of the cyst, and may include medications, surgery, or other interventions. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for individual cases.
Disclaimer: Each person’s journey is unique, treatment plan, life style, food habit, hormonal condition, immune system, chronic disease condition, previous medical history is also unique. So always seek the best advice from a qualified medical professional or health care provider before trying any treatments to ensure to find out the best plan for you. This guide is for general information and educational purposes only. If you or someone are suffering from this disease condition bookmark this website or share with someone who might find it useful! Boost your knowledge and stay ahead in your health journey. Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the article.









