Thyroid function tests (TFTs) is a collective term for blood tests used to check the function of the thyroid. TFTs may be requested if a patient is thought to suffer from hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), or to monitor the effectiveness of either thyroid-suppression or hormone replacement therapy. It is also requested routinely in conditions linked to thyroid diseases, such as atrial fibrillation and anxiety disorder. A TFT panel typically includes thyroid hormones such as thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin) and thyroxine (T4), and triiodothyronine (T3) depending on local laboratory policy.
The thyroid gland produces hormones that are essential for normal body metabolism. Blood testing is now commonly available to determine the adequacy of the levels of thyroid hormones. These blood tests can define whether the thyroid gland’s hormone production is normal, overactive, or underactive.
Thyroid hormone regulation- the chain of command
The thyroid itself is regulated by another gland that is located in the brain, called the pituitary. In turn, the pituitary is regulated in part by the thyroid (via a “feedback” effect of thyroid hormone on the pituitary gland) and by another gland called the hypothalamus.
The hypothalamus releases a hormone called thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which sends a signal to the pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). In turn, TSH sends a signal to the thyroid to release thyroid hormones. If a disruption occurs at any of these levels, a defect in thyroid hormone production may result in a deficiency of thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism).
Hypothalamus – TRH
↓
Pituitary – TSH
↓
Thyroid – T4 and T3
The rate of thyroid hormone production is controlled by the pituitary gland. If there is an insufficient amount of thyroid hormone circulating in the body to allow for normal functioning, the release of TSH is increased by the pituitary gland in an attempt to stimulate more thyroid hormone production
Thyroid function tests help to determine if your thyroid is not working correctly:
- hyperthyroid – an over-working thyroid
- hypothyroid – poor thyroid function
Symptoms of Hyperthyroid
The symptoms of hyperthyroidism include the following
- fatigue or muscle weakness
- hand tremors
- Excessive sweating
- Heat intolerance
- Increased bowel movements
- Tremor (usually fine shaking)
- mood swings
- increased appetite
- nervousness
- restlessness
- inability to concentrate
- irregular heartbeat
- difficulty sleeping
- fine, brittle hair, itching, hair loss
- nausea and vomiting
- breast development in men
- dizziness
- shortness of breath
- loss of consciousness
- fast, irregular heart rate
- nervousness or anxiety
- rapid heartbeat
- skin dryness
- trouble sleeping
- weight loss
- increased frequency of bowel movements
- light periods or skipping periods.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
- Fatigue
- Weight gain or increased difficulty losing weight
- Coarse, dry hair
- Dry, rough pale skin ,Hair loss
- Cold intolerance (you can’t tolerate cold temperatures like those around you)
- Muscle cramps and frequent muscle aches
- Constipation
- Irritability
- Memory loss
- Abnormal menstrual cycles
- Decreased libido
- Increased sensitivity to cold
- Elevated blood cholesterol level
- Muscle aches, tenderness and stiffness
- Pain, stiffness or swelling in your joints
- Heavier than normal or irregular menstrual periods
- Thinning hair
- Slowed heart rate
- Depression
- Impaired memory
Test overall
| Test | Abbreviation | Typical Ranges |
|---|---|---|
| Serum thyroxine | T4 | 4.6-12 ug/dl |
| Free thyroxine fraction | FT4F | 0.03-0.005% |
| Free Thyroxine | FT4 | 0.7-1.9 ng/dl |
| Thyroid hormone binding ratio | THBR | 0.9-1.1 |
| Free Thyroxine index | FT4I | 4-11 |
| Serum Triiodothyronine | T3 | 80-180 ng/dl |
| Free Triiodothyronine l | FT3 | 230-619 pg/d |
| Free T3 Index | FT3I | 80-180 |
| Radioactive iodine uptake | RAIU | 10-30% |
| Serum thyrotropin | TSH | 0.5-6 uU/ml |
| Thyroxine-binding globulin | TBG | 12-20 ug/dl T4 +1.8 ugm |
| TRH stimulation test Peak | TSH | 9-30 uIU/ml at 20-30 min |
| Serum thyroglobulin l | Tg | 0-30 ng/m |
| Thyroid microsomal antibody titer | TMAb | Varies with method |
| Thyroglobulin antibody titer | TgAb | Varies with method |
Thyroid hormones
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin)
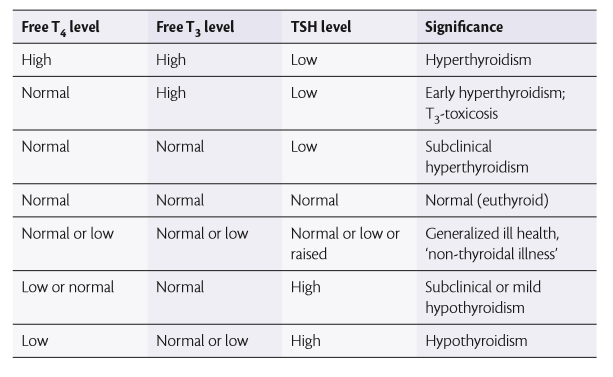
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin) is generally increased in hypothyroidism and decreased in hyperthyroidism.
Its measurement is the most sensitive test for thyroid hormone function. TSH is produced in the pituitary gland. The production of TSH is controlled by thyrotropin-releasing hormone(TRH), which is produced in the hypothalamus. TSH levels may be suppressed by excess free T3 (fT3) or free T4 (fT4) in the blood.
Total thyroxine(Total T4)
Total thyroxine is rarely measured, having been largely superseded by free thyroxine tests. Total thyroxine (Total T4) is generally elevated in hyperthyroidism and decreased in hypothyroidism. It is usually slightly elevated in pregnancy secondary to increased levels of thyroid-binding globulin (TBG).
Total T4 is measured to see the bound and unbound levels of T4. The total T4 is less useful in cases where there could be protein abnormalities. The total T4 is less accurate due to a large amount of T4 that is bound. The total T3 is measured in clinical practice since the T3 has decreased amount that is bound as compared to T4.
Reference ranges depend on the method of analysis. Results should always be interpreted using the range from the laboratory that performed the test. Example values are
| Lower limit | Upper limit | Unit |
| 4, 5.5 | 11, 12.3 | μg/dL |
| 60 | 140,160 | nmol/L |
Free thyroxine (fT4)
Free thyroxine (fT4) is generally elevated in hyperthyroidism and decreased in hypothyroidism.
Reference ranges depend on the method of analysis. Results should always be interpreted using the range from the laboratory that performed the test. Example values are
| Patient type | Lower limit | Upper limit | Unit |
| Normal adult | 0.7, 0.8 | 1.4, 1.5,1.8 | ng/dL |
| 9, 10, 12 | 18, 23 | pmol/L | |
| Infant 0–3 d | 2.0 | 5.0 | ng/dL |
| 26 | 65 | pmol/L | |
| Infant 3–30 d | 0.9 | 2.2 | ng/dL |
| 12 | 30 | pmol/L | |
| Child/Adolescent 31 d – 18 y |
0.8 | 2.0 | ng/dL |
| 10 | 26 | pmol/L | |
| Pregnant | 0.5 | 1.0 | ng/dL |
| 6.5 | 13 | pmol/L |
Total triiodothyronine (Total T3)
Total triiodothyronine (Total T3) is rarely measured, having been largely superseded by free T3 tests. Total T3 is generally elevated in hyperthyroidism and decreased in hypothyroidism.
Reference ranges depend on the method of analysis. Results should always be interpreted using the range from the laboratory that performed the test. Example values are:
| Test | Lower limit | Upper limit | Unit |
| Total triiodothyronine | 60, 75 | 175, 181 | ng/dL |
| 0.9, 1.1 | 2.5,2.7 | nmol/L |
Free triiodothyronine(fT3)
Free triiodothyronine (fT3) is generally elevated in hyperthyroidism and decreased in hypothyroidism.
Reference ranges depend on the method of analysis. Results should always be interpreted using the range from the laboratory that performed the test. Example values are:
| Patient type | Lower limit | Upper limit | Unit |
| Normal adult | 3.0 | 7.0 | pg/mL |
| 3.1 | 7.7 | pmol/L | |
| Children 2–16 y | 3.0 | 7.0 | pg/mL |
| 1.5 | 15.2 | pmol/L |
Carrier proteins
Thyroxine-binding globulin
An increased thyroxine-binding globulin results in increased total thyroxine and total triiodothyronine without an actual increase in the hormonal activity of thyroid hormones.
Reference ranges:
| Lower limit | Upper limit | Unit |
| 12 | 30 | mg/L |
Thyroglobulin
Reference ranges
| Lower limit | Upper limit | Unit |
| 1.5 | 30 | pmol/L |
| 1 | 20 | μg/L |
Other binding hormones
- Transthyretin (prealbumin)
- Albumin
Protein binding function
Thyroid hormone uptake(Tuptake or T3 uptake)
Thyroid hormone uptake (Tuptake or T3 uptake) is a measure of the unbound thyroxine-binding globulins in the blood, that is, the TBG that is unsaturated with thyroid hormone. Unsaturated TBG increases with decreased levels of thyroid hormones. It is not directly related to triiodothyronine, despite the name T3 uptake.
Reference ranges
| Patient type | Lower limit | Upper limit | Unit |
| Females | 25 | 35 | % |
| In pregnancy | 15 | 25 | % |
| Males | 25 | 35 | % |
Other protein binding tests
- Thyroid Hormone Binding Ratio(THBR)
- Thyroxine-binding index (TBI)
References