Thrombocytopenia is a condition in which you have a low blood platelet count. Platelets (thrombocytes) are colorless blood cells that help blood clot. Platelets stop bleeding by clumping and forming plugs in blood vessel injuries.
Thrombocytopenia might occur as a result of a bone marrow disorder such as leukemia or an immune system problem. Or it can be a side effect of taking certain medications. It affects both children and adults.
Thrombocytopenia can be mild and cause few signs or symptoms. In rare cases, the number of platelets can be so low that dangerous internal bleeding occurs. Treatment options are available.
Thrombocytopenia signs and symptoms may include:
- Easy or excessive bruising (purpura)
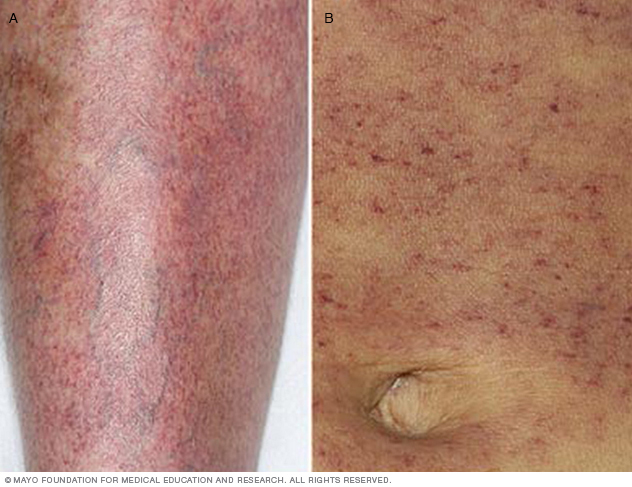
- Superficial bleeding into the skin that appears as a rash of pinpoint-sized reddish-purple spots (petechiae), usually on the lower legs
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts
- Bleeding from your gums or nose
- Blood in urine or stools
- Unusually heavy menstrual flows
- Fatigue
- Enlarged spleen
When to see a doctor
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have signs of thrombocytopenia that worry you.
Bleeding that won’t stop is a medical emergency. Seek immediate help for bleeding that can’t be controlled by the usual first-aid techniques, such as applying pressure to the area.
Diagnostic Tests for TTP:
To diagnose TTP, doctors may use several tests to examine your blood and rule out other conditions. Some common diagnostic tests include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This measures the number of platelets in your blood, which is usually low in TTP.
- Blood Smear: A microscopic examination of your blood to check for abnormal cells.
- ADAMTS13 Activity Test: This test checks the activity of the ADAMTS13 protein.
- Kidney Function Tests: TTP can affect kidney function, so these tests help assess kidney health.
- Coagulation Tests: To evaluate how your blood clots.
Treatment for TTP:
Treatment for TTP aims to stop the formation of blood clots and manage symptoms. Here are some common treatments:
- Plasma Exchange (Plasmapheresis): This procedure removes and replaces the plasma in your blood, which can help remove harmful antibodies and improve clotting.
- Steroids: Medications like corticosteroids may be prescribed to suppress the immune system’s response.
- Immune Globulin: Intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) may be given to boost the immune system.
- Rituximab: This medication can help reduce the autoimmune response.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove clots or damaged tissue.
Drugs Used in TTP Treatment:
Several medications may be used to treat TTP and manage its symptoms. Here are some commonly prescribed drugs:
- Prednisone: A steroid that reduces inflammation.
- Plavix (Clopidogrel): Helps prevent platelets from sticking together.
- Soliris (Eculizumab): A medication that targets the immune system to reduce the risk of TTP episodes.
- Rituxan (Rituximab): Suppresses the immune response.
- Immune Globulin (IVIG): Boosts the immune system’s ability to fight TTP.
Conclusion:
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) is a rare but serious blood disorder that can affect anyone. While it may seem complex at first, understanding its types, causes, symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment options is essential for early detection and effective management.
If you or someone you know experiences TTP symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. With proper diagnosis and treatment, TTP can be managed, and its impact on your health minimized. Remember, knowledge is power, and being informed about TTP can make a significant difference in your or your loved one’s journey to recovery.
Disclaimer: Each person’s journey is unique, treatment plan, life style, food habit, hormonal condition, immune system, chronic disease condition, previous medical history is also unique. So always seek the best advice from a qualified medical professional or health care provider before trying any treatments to ensure to find out the best plan for you. This guide is for general information and educational purposes only. If you or someone are suffering from this disease condition bookmark this website or share with someone who might find it useful! Boost your knowledge and stay ahead in your health journey. Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the article.







