What Is Teres Minor?/Teres Minor is a narrow elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule.[rx]
The primary function of the teres minor is to modulate the action of the deltoid, preventing the humeral head from sliding upward as the arm is abducted. It also functions to rotate the humerus laterally. The teres minor is innervated by the axillary nerve.[rx]
At a Glance of Teres minor
-
Function – Lateral rotation of the arm, stabilize glenohumeral joint
-
Origin – Lateral/axillary border and adjacent posterior aspect of the scapula
-
Insertion – Inferior aspect of the greater tubercle on the humerus
-
Innervation – Axillary nerve (C5, C6)
[stextbox id=’custom’ defcaption=”true”]
| Muscles on the dorsum of the left scapula, and the Triceps brachii muscle: | |
| Details | |
|---|---|
| Origin | the lateral border of the scapula |
| Insertion | inferior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus |
| Artery | posterior circumflex humeral artery and the circumflex scapular artery |
| Nerve | axillary nerve (C5-C6) |
| Actions | laterally rotates the arm, stabilizes the humerus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus teres minor |
| TA | A04.6.02.010 |
| FMA | 32550 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
[/stextbox]
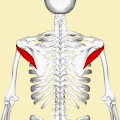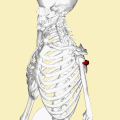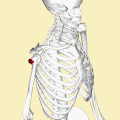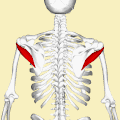
Nerve Supply of Teres Minor
The muscle is innervated by the posterior branch of the axillary nerve where it forms a pseudoganglion.[rx] A pseudoganglion has no nerve cells but nerve fibers are present. Damage to the fibers innervating the teres minor is clinically significant. Sometimes a group of muscle fibers from teres minor may be fused with infraspinatus.
Functions of Teres Minor
The infraspinatus and teres minor attach to the head of the humerus; as part of the rotator cuff, they help hold the humeral head in the glenoid cavity of the scapula. They work in tandem with the posterior deltoid to externally (laterally) rotate the humerus, as well as adduction. Teres Minor can produce only very small scapular plane adduction during maximal contraction with an adductor moment arm of approximately 0.2 cm at 45° of shoulder internal rotation and approximately 0.1 cm at 45° of shoulder external rotation.
References








