PHP is a server-side scripting language. that is used to develop Static websites or Dynamic websites or Web applications. PHP stands for Hypertext Pre-processor, which earlier stood for Personal Home Pages.
PHP scripts can only be interpreted on a server that has PHP installed. The client computers accessing the PHP scripts require a web browser only. A PHP file contains PHP tags and ends with the extension “.php”.
What is a Scripting Language?
A script is a set of programming instructions that are interpreted at runtime.
A scripting language is a language that interprets scripts at runtime. Scripts are usually embedded into other software environments. The purpose of the scripts is usually to enhance the performance or perform routine tasks for an application. Server-side scripts are interpreted on the server while client-side scripts are interpreted by the client application.
PHP is a server-side script that is interpreted on the server while JavaScript is an example of a client-side script that is interpreted by the client browser. Both PHP and JavaScript can be embedded into HTML pages.
Programming Language Vs Scripting Language
| Programming language | Scripting language |
|---|---|
| Has all the features needed to develop complete applications? | Mostly used for routine tasks |
| The code has to be compiled before it can be executed | The code is usually executed without compiling |
| Does not need to be embedded into other languages | Is usually embedded into other software environments. |
What does PHP stand for?
PHP means – Personal Home Page, but it now stands for the recursive backronym PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor.
PHP code may be embedded into HTML code, or it can be used in combination with various web template systems, web content management system,s and web frameworks.
PHP Syntax
![]()
A PHP file can also contain tags such as HTML and client-side scripts such as JavaScript.
- HTML is an added advantage when learning PHP Language. You can even learn PHP without knowing HTML but it’s recommended you at least know the basics of HTML.
- Database management systems DBMS for database-powered applications.
- For more advanced topics such as interactive applications and web services, you will need JavaScript and XML.
The flowchart diagram shown below illustrates the basic architecture of a PHP web application and how the server handles the requests.
Why use PHP?
You have obviously heard of a number of programming languages out there; you may be wondering why we would want to use PHP as our poison for web programming. Below are some of the compelling reasons.
- PHP is open-source and free.
- Short learning curve compared to other languages such as JSP, ASP, etc.
- Large community document
- Most web hosting servers support PHP by default unlike other languages such as ASP that need IIS. This makes PHP a cost-effective choice.
- PHP is regularly updated to keep abreast of the latest technology trends.
- Another benefit that you get with PHP is that it’s a server-side scripting language; this means you only need to install it on the server and client computers requesting resources from the server do not need to have PHP installed; only a web browser would be enough.
- PHP has inbuilt support for working hand in hand with MySQL; this doesn’t mean you can’t use PHP with other database management systems. You can still use PHP with
- Postgres
- Oracle
- MS SQL Server
- ODBC etc.
- PHP is cross-platform; this means you can deploy your application on a number of different operating systems such as Windows, Linux, Mac OS, etc.
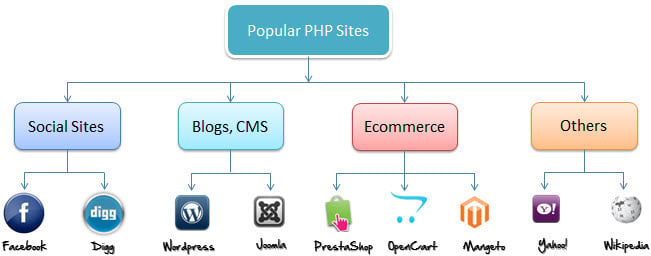
What is PHP used for & Market share?
In terms of market share, there are over 20 million websites and applications on the internet developed using PHP scripting language.
This may be attributed to the points raised above;
The diagram below shows some of the popular sites that use PHP
PHP vs Asp.Net VS JSP VS CFML
ASP – Active Server Pages, JSP – Java Server Pages, CFML – Cold Fusion Markup language The table below compares the various server-side scripting languages with PHP
| FEATURE | PHP | ASP | JSP | CFML |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning curve | short | Longer than PHP | Longer than PHP | Longer than PHP |
| Web hosting | Supported by almost all hosting servers | Needs dedicated server | Fairly supported | Needs dedicated server |
| Open-source | Yes | No | Yes | Both commercial and open-source |
| Web services support | Built-in | Uses the .NET framework | Uses add on libraries | Built-in |
| Integration with HTML | Easy | Fairly complex | Fairly complex | Easy |
| MySQL support | Native | Needs third-party drivers | Needs third-party drivers | The current version has native support. Older versions use ODBC |
| Easily extended by other languages | Yes | No | Extended using Java classes and libraries. | Yes |
PHP File Extensions
File extension and Tags In order for the server to identify our PHP files and scripts, we must save the file with the “.php” extension. Older PHP file extensions include
- .phtml
- .php3
- .php4
- .php5
- .phps
PHP was designed to work with HTML, and as such, it can be embedded into the HTML code.
You can create PHP files without any HTML tags and that is called a Pure PHP file.
The server interprets the PHP code and outputs the results as HTML code to the web browsers.
In order for the server to identify the PHP code from the HTML code, we must always enclose the PHP code in PHP tags.
A PHP tag starts with the less than symbol followed by the question mark and then the words “PHP”.
PHP is a case-sensitive language, “VAR” is not the same as “var”.
The PHP tags themselves are not case-sensitive, but it is strongly recommended that we use lower case letters. The code below illustrates the above point.
<?php … ?>
We will be referring to the PHP lines of code as statements. PHP statements end with a semi-colon (;). If you only have one statement, you can omit the semi-colon. If you have more than one statement, then you must end each line with a semi-colon. For the sake of consistency, it is recommended that you always end your statement(s) with a semi-colon. PHP scripts are executed on the server. The output is returned in form of HTML.
FAQ and Top 100 PHP Interview Questions and Answers
1) What is PHP?
PHP is a web language based on scripts that allow developers to dynamically create generated web pages.
2) What do the initials of PHP stand for?
PHP means PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor.
3) Which programming language does PHP resemble?
PHP syntax resembles Perl and C
4) What does PEAR stand for?
PEAR means “PHP Extension and Application Repository”. It extends PHP and provides a higher level of programming for web developers.
5) What is the actually used PHP version?
Version 7.1 or 7.2 is the recommended version of PHP.
6) How do you execute a PHP script from the command line?
Just use the PHP command line interface (CLI) and specify the file name of the script to be executed as follows:
php script.php
7) How to run the interactive PHP shell from the command line interface?
Just use the PHP CLI program with the option -a as follows:
php -a
8) What is the correct and the most two common way to start and finish a PHP block of code?
The two most common ways to start and finish a PHP script are:
<?php [ --- PHP code---- ] ?> and <? [--- PHP code ---] ?>
9) How can we display the output directly to the browser?
To be able to display the output directly to the browser, we have to use the special tags <?= and ?>.
10) What is the main difference between PHP 4 and PHP 5?
PHP 5 presents many additional OOP (Object Oriented Programming) features.
11) Is multiple inheritance supported in PHP?
PHP supports only single inheritance; it means that a class can be extended from only one single class using the keyword ‘extended’.
12) What is the meaning of a final class and a final method?
‘final’ is introduced in PHP5. Final class means that this class cannot be extended and a final method cannot be overridden.
13) How is the comparison of objects done in PHP?
We use the operator ‘==’ to test is two objects are instanced from the same class and have the same attributes and equal values. We can test if two objects are referring to the same instance of the same class by the use of the identity operator ‘===’.
14) How can PHP and HTML interact?
It is possible to generate HTML through PHP scripts, and it is possible to pass pieces of information from HTML to PHP.
15) What type of operation is needed when passing values through a form or an URL?
If we would like to pass values through a form or an URL, then we need to encode and decode them using htmlspecialchars() and urlencode().
16) How can PHP and Javascript interact?
PHP and Javascript cannot directly interact since PHP is a server-side language and Javascript is a client-side language. However, we can exchange variables since PHP can generate Javascript code to be executed by the browser and it is possible to pass specific variables back to PHP via the URL.
17) What is needed to be able to use the image function?
GD library is needed to execute image functions.
18) What is the use of the function ‘image types()’?
image types() give the image format and types supported by the current version of GD-PHP.
19) What are the functions to be used to get the image’s properties (size, width, and height)?
The functions are getimagesize() for size, imagesx() for width and imagesy() for height.
20) How failures in execution are handled with include() and require() functions?
If the function require() cannot access the file then it ends with a fatal error. However, the include() function gives a warning, and the PHP script continues to execute.
21) What is the main difference between require() and require_once()?
require(), and require_once() perform the same task except that the second function checks if the PHP script is already included or not before executing it.
(same for include_once() and include())
22) How can I display text with a PHP script?
Two methods are possible:
<!--?php echo "Method 1"; print "Method 2"; ?-->
23) How can we display information of a variable and readable by a human with PHP?
To be able to display a human-readable result we use print_r().
24) How is it possible to set an infinite execution time for a PHP script?
The set_time_limit(0) added at the beginning of a script sets to infinite the time of execution to not have the PHP error ‘maximum execution time exceeded.’ It is also possible to specify this in the php.ini file.
25) What does the PHP error ‘Parse error in PHP – unexpected T_variable at line x’ mean?
This is a PHP syntax error expressing that a mistake at the line x stops parsing and executing the program.
26) What should we do to be able to export data into an Excel file?
The most common and used way is to get data into a format supported by Excel. For example, it is possible to write a .csv file, to choose for example comma as a separator between fields and then to open the file with Excel.
27) What is the function file_get_contents() useful for?
file_get_contents() lets reading a file and storing it in a string variable.
28) How can we connect to a MySQL database from a PHP script?
To be able to connect to a MySQL database, we must use the mysqli_connect() function as follows:
<!--?php $database = mysqli_connect("HOST", "USER_NAME", "PASSWORD"); mysqli_select_db($database,"DATABASE_NAME"); ?-->
29) What is the function mysql_pconnect() useful for?
mysql_pconnect() ensure a persistent connection to the database, it means that the connection does not close when the PHP script ends.
This function is not supported in PHP 7.0 and above
30) How be the result set of Mysql handled in PHP?
The result set can be handled using mysqli_fetch_array, mysqli_fetch_assoc, mysqli_fetch_object or mysqli_fetch_row.
31) How is it possible to know the number of rows returned in the result set?
The function mysqli_num_rows() returns the number of rows in a result set.
32) Which function gives us the number of affected entries by a query?
mysqli_affected_rows() return the number of entries affected by an SQL query.
33) What is the difference between mysqli_fetch_object() and mysqli_fetch_array()?
The mysqli_fetch_object() function collects the first single matching record where mysqli_fetch_array() collects all matching records from the table in an array.
34) How can we access the data sent through the URL with the GET method?
To access the data sent via the GET method, we use $_GET array like this:
www.url.com?var=value $variable = $_GET["var"]; this will now contain 'value'
35) How can we access the data sent through the URL with the POST method?
To access the data sent this way, you use the $_POST array.
Imagine you have a form field called ‘var’ on the form when the user clicks submit to the post form, you can then access the value like this:
$_POST["var"];
36) How can we check the value of a given variable is a number?
It is possible to use the dedicated function, is_numeric() to check whether it is a number or not.
37) How can we check the value of a given variable is alphanumeric?
It is possible to use the dedicated function, ctype_alnum to check whether it is an alphanumeric value or not.
38) How do I check if a given variable is empty?
If we want to check whether a variable has a value or not, it is possible to use the empty() function.
39) What does the unlink() function mean?
The unlink() function is dedicated to file system handling. It simply deletes the file given as an entry.
40) What does the unset() function mean?
The unset() function is dedicated for variable management. It will make a variable undefined.
41) How do I escape data before storing it in the database?
The addslashes function enables us to escape data before storing it in the database.
42) How is it possible to remove escape characters from a string?
The stripslashes function enables us to remove the escape characters before apostrophes in a string.
43) How can we automatically escape incoming data?
We have to enable the Magic quotes entry in the configuration file of PHP.
44) What does the function get_magic_quotes_gpc() means?
The function get_magic_quotes_gpc() tells us whether the magic quotes is switched on or no.
45) Is it possible to remove the HTML tags from data?
The strip_tags() function enables us to clean a string from the HTML tags.
46) what is the static variable in function useful for?
A static variable is defined within a function only the first time, and its value can be modified during function calls as follows:
<!--?php function testFunction() { static $testVariable = 1; echo $testVariable; $testVariable++; } testFunction();
//1 testFunction(); //2 testFunction(); //3 ?-->
47) How can we define a variable accessible in functions of a PHP script?
This feature is possible using the global keyword.
48) How is it possible to return a value from a function?
A function returns a value using the instruction ‘return $value;’.
49) What is the most convenient hashing method to be used to hash passwords?
It is preferable to use crypt() which natively supports several hashing algorithms or the function hash() which supports more variants than crypt() rather than using the common hashing algorithms such as md5, sha1, or sha256 because they are conceived to be fast. Hence, hashing passwords with these algorithms can create vulnerability.
50) Which cryptographic extension provide generation and verification of digital signatures?
The PHP-OpenSSL extension provides several cryptographic operations including generation and verification of digital signatures.
51) How is a constant defined in a PHP script?
The define() directive lets us define a constant as follows:
define ("ACONSTANT", 123);
52) How can you pass a variable by reference?
To be able to pass a variable by reference, we use an ampersand in front of it, as follows $var1 = &$var2
53) Will a comparison of an integer 12 and a string “13” work in PHP?
“13” and 12 can be compared in PHP since it casts everything to the integer type.
54) How is it possible to cast types in PHP?
The name of the output type has to be specified in parentheses before the variable which is to be cast as follows:
* (int), (integer) – cast to integer
* (bool), (boolean) – cast to boolean
* (float), (double), (real) – cast to float
* (string) – cast to string
* (array) – cast to array
* (object) – cast to object
55) When is a conditional statement ended with endif?
When the original if was followed by: and then the code block without braces.
56) How is the ternary conditional operator used in PHP?
It is composed of three expressions: a condition, and two operands describing what instruction should be performed when the specified condition is true or false as follows:
Expression_1?Expression_2 : Expression_3;
57) What is the function func_num_args() used for?
The function func_num_args() is used to give the number of parameters passed into a function.
58) If the variable $var1 is set to 10 and the $var2 is set to the character var1, what’s the value of $$var2?
$$var2 contains the value 10.
59) What does accessing a class via: mean?
:: is used to access static methods that do not require object initialization.
60) In PHP, objects are passed by value or by reference?
In PHP, objects are passed by reference.
61) Are Parent constructors called implicitly inside a class constructor?
No, a parent constructor has to be called explicitly as follows:
parent::constructor($value)
62) What’s the difference between __sleep and __wakeup?
__sleep returns the array of all the variables that need to be saved, while __wakeup retrieves them.
63) What is faster?
1- Combining two variables as follows:
$variable1 = 'Hello '; $variable2 = 'World'; $variable3 = $variable1.$variable2;
Or
2- $variable3 = "$variable1$variable2";
$variable3 will contain “Hello World”. The first code is faster than the second code especially for large sets of data.
64) what is the definition of a session?
A session is a logical object enabling us to preserve temporary data across multiple PHP pages.
65) How to initiate a session in PHP?
The use of the function session_start() lets us activate a session.
66) How can you propagate a session id?
You can propagate a session id via cookies or URL parameters.
67) What is the meaning of a Persistent Cookie?
A persistent cookie is permanently stored in a cookie file on the browser’s computer. By default, cookies are temporary and are erased if we close the browser.
68) When do sessions end?
Sessions automatically end when the PHP script finishes executing but can be manually ended using the session_write_close().
69) What is the difference between session_unregister() and session_unset()?
The session_unregister() function unregister a global variable from the current session and the session_unset() function frees all session variables.
70) What does $GLOBALS mean?
$GLOBALS is an associative array including references to all variables which are currently defined in the global scope of the script.
71) What does $_SERVER mean?
$_SERVER is an array including information created by the webserver such as paths, headers, and script locations.
72) What does $_FILES mean?
$_FILES is an associative array composed of items sent to the current script via the HTTP POST method.
73) What is the difference between $_FILES[‘user file’s][‘name’] and $_FILES[‘user file’s][‘tmp_name’]?
$_FILES[‘user file’s][‘name’] represents the original name of the file on the client machine,
$_FILES[‘user file’s][‘tmp_name’] represents the temporary filename of the file stored on the server.
74) How can we get the error when there is a problem uploading a file?
$_FILES[‘user file’s][‘error’] contains the error code associated with the uploaded file.
75) How can we change the maximum size of the files to be uploaded?
We can change the maximum size of files to be uploaded by changing upload_max_filesize in php.ini.
76) What does $_ENV mean?
$_ENV is an associative array of variables sent to the current PHP script via the environment method.
77) What does $_COOKIE mean?
$_COOKIE is an associative array of variables sent to the current PHP script using the HTTP Cookies.
78) What does the scope of variables mean?
The scope of a variable is the context within which it is defined. For the most part, all PHP variables only have a single scope. This single scope spans included and required files as well.
79) what is the difference between the ‘BITWISE AND’ operator and the ‘LOGICAL AND’ operator?
$a and $b: TRUE if both $a and $b are TRUE.
$a & $b: Bits that are set in both $a and $b are set.
80) What are the two main string operators?
The first is the concatenation operator (‘.’), which returns the concatenation of its right and left arguments. The second is (‘.=’), which appends the argument on the right to the argument on the left.
81) What does the array operator ‘===’ means?
$a === $b TRUE if $a and $b have the same key/value pairs in the same order and of the same types.
82) What is the differences between $a != $b and $a !== $b?
!= means inequality (TRUE if $a is not equal to $b) and !== means non-identity (TRUE if $a is not identical to $b).
83) How can we determine whether a PHP variable is an instantiated object of a certain class?
To be able to verify whether a PHP variable is an instantiated object of a certain class we use instanceof.
84) What is the goto statement useful for?
The goto statement can be placed to enable jumping inside the PHP program. The target is pointed by a label followed by a colon, and the instruction is specified as a goto statement followed by the desired target label.
85) what is the difference between Exception::getMessage and Exception:: getLine?
Exception::getMessage lets us get the Exception message and Exception::getLine lets us get the line in which the exception occurred.
86) What does the expression Exception::__toString mean?
Exception::__toString gives the String representation of the exception.
87) How is it possible to parse a configuration file?
The function parse_ini_file() enables us to load in the ini file specified in the filename and returns the settings in it in an associative array.
88) How can we determine whether a variable is set?
The boolean function is set determines if a variable is set and is not NULL.
89) What is the difference between the functions strstr() and stristr()?
The string function strstr(string all String, string occ) returns part of allString from the first occurrence of occ to the end of allString. This function is case-sensitive. stristr() is identical to strstr() except that it is case insensitive.
90) what is the difference between for and for each?
for is expressed as follows:
for (expr1; expr2; expr3)
statement
The first expression is executed once at the beginning. In each iteration, expr2 is evaluated. If it is TRUE, the loop continues, and the statements inside for are executed. If it evaluates to FALSE, the execution of the loop ends. expr3 is tested at the end of each iteration.
However, each provides an easy way to iterate over arrays, and it is only used with arrays and objects.
91) Is it possible to submit a form with a dedicated button?
It is possible to use the document.form.submit() function to submit the form. For example: <input type=button value=”SUBMIT” onClick=”document.form.submit()”>
92) What is the difference between ereg_replace() and eregi_replace()?
The function eregi_replace() is identical to the function ereg_replace() except that it ignores case distinction when matching alphabetic characters.
93) Is it possible to protect special characters in a query string?
Yes, we use the urlencode() function to be able to protect special characters.
94) What are the three classes of errors that can occur in PHP?
The three basic classes of errors are notices (non-critical), warnings (serious errors), and fatal errors (critical errors).
95) What is the difference between characters \034 and \x34?
\034 is octal 34 and \x34 is hex 34.
96) How can we pass the variable through the navigation between the pages?
It is possible to pass the variables between the PHP pages using sessions, cookies or hidden form fields.
97) Is it possible to extend the execution time of a PHP script?
The use of the set_time_limit(int seconds) enables us to extend the execution time of a PHP script. The default limit is 30 seconds.
98) Is it possible to destroy a cookie?
Yes, it is possible by setting the cookie with a past expiration time.
99) What is the default session time in PHP?
The default session time in PHP is until the closing of the browser
100) Is it possible to use the COM component in PHP?
Yes, it’s possible to integrate (Distributed) Component Object Model components ((D)COM) in PHP scripts which is provided as a framework.
101) Explain whether it is possible to share a single instance of a Memcache between multiple PHP projects?
Yes, it is possible to share a single instance of Memcache between multiple projects. Memcache is a memory store space, and you can run Memcache on one or more servers. You can also configure your client to speak to a particular set of instances. So, you can run two different Memcache processes on the same host, and yet they are completely independent. Unless, if you have partitioned your data, then it becomes necessary to know from which instance to get the data from or to put it into.
102) Explain how you can update Memcached when you make changes to PHP?
When PHP changes you can update Memcached by
- Clearing the Cache proactively: Clearing the cache when an insert or update is made
- Resetting the Cache: It is similar to the first method but rather than just deleting the keys and waiting for the next request for the data to refresh the cache, reset the values after the insert or update.