Calyceal cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the calyces, which are the cup-shaped structures in the kidney. These structures help collect urine from the kidney and direct it to the renal pelvis, where it then flows into the ureter.
Pathophysiology
Structure:
- Kidneys: Two bean-shaped organs that filter blood and produce urine.
- Calyces: The areas in the kidney where urine collects.
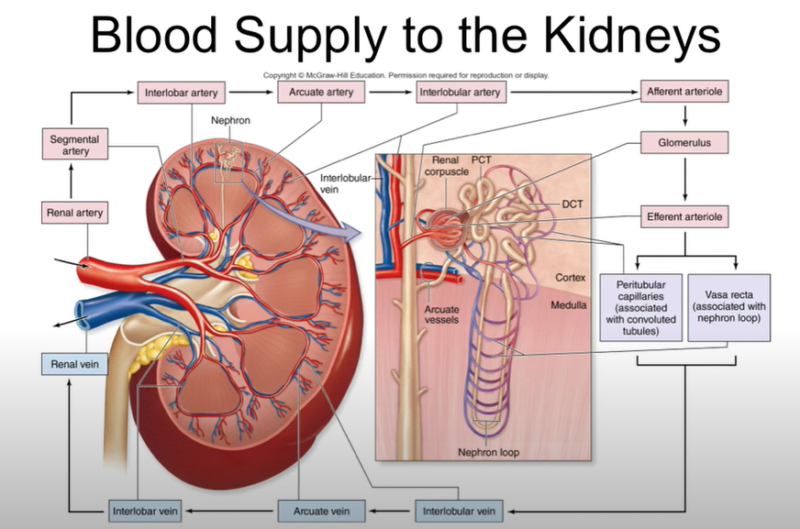
Blood Supply:
- The renal arteries supply blood to the kidneys. Cancer can disrupt this blood flow, affecting kidney function.
Nerve Supply:
- The kidneys receive nerve supply from the autonomic nervous system, which can influence kidney function and pain perception.
Types of Calyceal Cancer
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): The most common type of kidney cancer, which can affect the calyces.
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma: Often starts in the renal pelvis but can invade calyceal structures.
- Sarcoma: A rare type of cancer that can occur in the kidney’s soft tissues.
- Lymphoma: Cancer that begins in the lymphatic system and can affect the kidneys.
Causes of Calyceal Cancer
- Smoking: Increases risk significantly.
- Obesity: Linked to kidney cancer.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can contribute to cancer development.
- Family History: Genetic predisposition can play a role.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Increases cancer risk.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Such as asbestos or cadmium.
- Age: Risk increases with age.
- Gender: More common in men.
- Race: Higher incidence in African Americans.
- Diabetes: Associated with higher risk.
- Viral Infections: Such as hepatitis C.
- Exposure to Radiation: Previous radiation therapy can increase risk.
- Hormonal Factors: Certain hormone imbalances may contribute.
- Diet: High-fat, low-fiber diets may increase risk.
- Kidney Stones: Chronic irritation may lead to cancer.
- Congenital Kidney Diseases: Such as polycystic kidney disease.
- Tuberculosis: Renal tuberculosis can increase cancer risk.
- Environmental Pollutants: Prolonged exposure can be harmful.
- Previous Cancer History: History of other cancers may increase risk.
- Genetic Mutations: Certain inherited mutations may predispose individuals.
Symptoms of Calyceal Cancer
- Blood in Urine (Hematuria): Often the first sign.
- Persistent Back Pain: Pain near the kidneys.
- Abdominal Mass: A lump in the abdomen.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness without reason.
- Loss of Appetite: Decreased desire to eat.
- Night Sweats: Excessive sweating at night.
- Fever: Low-grade fever can occur.
- Frequent Urination: Needing to urinate more often.
- Painful Urination: Discomfort during urination.
- Swelling in the Legs or Ankles: Fluid retention may occur.
- Nausea: Feeling sick to the stomach.
- Vomiting: May occur alongside nausea.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing.
- Constipation: Digestive issues may arise.
- Anemia: Low red blood cell count leading to fatigue.
- Weakness: Generalized weakness.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin or eyes.
- Bloating: Abdominal swelling.
- Bone Pain: If cancer spreads to bones.
Diagnostic Tests for Calyceal Cancer
- Urinalysis: Tests for blood or cancer cells in urine.
- CT Scan: Detailed images of the kidneys and surrounding structures.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging for soft tissue evaluation.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to visualize kidneys.
- X-rays: Can identify abnormalities in the kidneys.
- Kidney Biopsy: Sample of kidney tissue to check for cancer.
- Blood Tests: To assess kidney function and detect cancer markers.
- Cystoscopy: Direct visualization of the bladder and urethra.
- PET Scan: Shows areas of high metabolic activity, indicating cancer.
- Bone Scan: Detects cancer spread to bones.
- Angiography: Looks at blood vessels in the kidneys.
- Genetic Testing: Identifies inherited mutations.
- Staging Tests: Determine the extent of cancer.
- Liver Function Tests: Checks for liver involvement.
- Electrolyte Levels: Assesses kidney function.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Checks overall health.
- Metabolic Panel: Assesses kidney and metabolic function.
- Urine Cytology: Examines urine for abnormal cells.
- Imaging with Contrast: Enhances visibility of structures.
- Dermatological Examination: Checks for skin manifestations of syndromes related to kidney cancer.
Non-Pharmacological Treatments
- Dietary Changes: Healthy eating habits.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Regular Exercise: Helps improve overall health.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga or meditation.
- Nutritional Supplements: Vitamins and minerals as advised.
- Acupuncture: May help manage symptoms.
- Massage Therapy: Relieves stress and discomfort.
- Physical Therapy: Improves mobility and strength.
- Counseling: Mental health support.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges.
- Mindfulness Practices: Enhances emotional well-being.
- Herbal Remedies: Consult a professional for guidance.
- Homeopathy: Alternative therapy approaches.
- Chiropractic Care: Helps with physical alignment.
- Biofeedback: Helps manage stress responses.
- Art or Music Therapy: Enhances emotional expression.
- Avoiding Tobacco and Alcohol: Reduces risk factors.
- Lifestyle Modification: Changes to improve health.
- Complementary Therapies: Other holistic practices.
Drugs for Calyceal Cancer
- Targeted Therapy Drugs: Such as sunitinib (Sutent).
- Immunotherapy: Nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda).
- Chemotherapy Agents: Such as doxorubicin and gemcitabine.
- Hormonal Therapy: Anti-androgens in certain cases.
- Bone-targeted agents: Bisphosphonates for bone health.
- Analgesics: For pain management.
- Anti-nausea Medications: To manage side effects of treatment.
- Steroids: To reduce inflammation.
- Antidepressants: For mood support.
- Antibiotics: To prevent or treat infections.
- Antihypertensives: For managing blood pressure.
- Anticoagulants: If blood clots are a concern.
- Vitamin D supplements: For bone health.
- Erythropoietin: To boost red blood cell production.
- Blood thinners: To prevent clotting issues.
- Analgesic patches: For localized pain relief.
- Topical agents: For skin-related issues.
- Flu vaccine: To prevent illness during treatment.
- Proton pump inhibitors: For stomach protection.
- Gastroprotective agents: For digestive health.
Surgical Options for Calyceal Cancer
- Partial Nephrectomy: Removing the tumor while preserving kidney function.
- Radical Nephrectomy: Complete removal of the affected kidney.
- Lymph Node Dissection: Removing nearby lymph nodes.
- Calyceal Resection: Targeted removal of the calyx with the tumor.
- Nephrectomy with Adrenalectomy: Removing the kidney along with the adrenal gland.
- Cryoablation: Freezing cancer cells to kill them.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Heating cancer cells to destroy them.
- Transurethral Resection: Removing tumors via the urinary tract.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Minimally invasive techniques using robotics.
- Palliative Surgery: To relieve symptoms in advanced cases.
Prevention of Calyceal Cancer
- Quit Smoking: Reducing the risk significantly.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Prevent obesity.
- Regular Check-ups: Monitor kidney health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water.
- Healthy Diet: High in fruits and vegetables.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Moderation is key.
- Control Blood Pressure: Keep hypertension in check.
- Manage Diabetes: Control blood sugar levels.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity is crucial.
- Avoid Exposure to Toxins: Reduce contact with harmful substances.
- Protect from Radiation: Limit unnecessary exposure.
- Genetic Counseling: For those with a family history.
- Use Protective Equipment: If working with chemicals.
- Stay Informed About Health Risks: Know your personal risk factors.
- Engage in Regular Screening: Especially if at higher risk.
- Vaccination: Stay up-to-date on relevant vaccines.
- Healthy Gut: Maintain digestive health.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Limit intake of unhealthy fats.
- Support Healthy Kidney Function: Through lifestyle choices.
- Regular Monitoring for High-risk Individuals: More frequent check-ups.
When to See a Doctor
- If you experience blood in your urine.
- Persistent back pain that doesn’t go away.
- Unexplained weight loss or appetite loss.
- Any unusual lumps or swelling in the abdomen.
- Recurring fever or night sweats.
- Symptoms of kidney infection (painful urination, frequent urination).
- Chronic fatigue that affects daily life.
- Symptoms of anemia (pale skin, weakness).
- If you have risk factors and notice any changes in your health.
- Regular check-ups if you have a family history of kidney disease or cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is calyceal cancer?
- A type of kidney cancer affecting the calyces.
- What causes calyceal cancer?
- Factors include smoking, obesity, and genetic predisposition.
- What are the symptoms?
- Symptoms include blood in urine, back pain, and weight loss.
- How is it diagnosed?
- Diagnosed through imaging tests, urinalysis, and biopsies.
- What treatments are available?
- Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
- Can calyceal cancer be prevented?
- Lifestyle changes can reduce the risk.
- What should I do if I have symptoms?
- Consult a healthcare provider immediately.
- Is calyceal cancer curable?
- Early detection improves the chances of successful treatment.
- What is the survival rate?
- Survival rates vary based on stage and overall health.
- How does smoking affect kidney health?
- Smoking significantly increases the risk of kidney cancer.
- Can diet influence cancer risk?
- Yes, a healthy diet can help lower risk.
- What role does genetics play?
- Family history can increase risk.
- Are there support groups for patients?
- Yes, many organizations provide support for cancer patients.
- How often should I get screened?
- Discuss with your doctor, especially if at high risk.
- What are the side effects of treatment?
- Side effects vary; common ones include fatigue, nausea, and pain.
Conclusion
Calyceal cancer is a serious condition, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health. Regular check-ups and healthy lifestyle choices play a crucial role in prevention and early detection. If you experience any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly.







