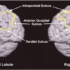
The supramarginal gyrus is a part of your brain that plays a crucial role in various functions like language processing, social cognition, and sensory integration. Disorders affecting this area can lead to significant challenges in daily life. In this guide, we’ll explore different aspects of supramarginal gyrus disorders, including types, causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatments, medications, surgeries, preventions, and when to seek medical help.
Types of Supramarginal Gyrus Disorders:
- Aphasia: Difficulty with language comprehension and expression.
- Apraxia: Difficulty with coordinated movements, like using tools or gestures.
- Dyscalculia: Difficulty with understanding and manipulating numbers.
- Dyslexia: Difficulty with reading and interpreting written language.
- Social Cognition Disorders: Challenges in understanding social cues and interactions.
Causes of Supramarginal Gyrus Disorders:
- Brain Injury: Trauma to the head can damage the supramarginal gyrus.
- Stroke: Interruption of blood flow to the brain can lead to tissue damage.
- Brain Tumors: Abnormal growths in the brain can affect nearby areas, including the supramarginal gyrus.
- Neurological Diseases: Conditions like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease can impact brain function.
- Genetic Factors: Some disorders may have a hereditary component.
- Developmental Abnormalities: Problems during brain development can lead to lifelong issues.
- Infections: Certain infections affecting the brain can cause damage to specific areas.
- Toxic Exposure: Exposure to toxins or chemicals can harm brain tissue.
- Metabolic Disorders: Imbalances in metabolic processes can affect brain function.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions where the immune system attacks healthy tissue can impact brain function.
Symptoms of Supramarginal Gyrus Disorders:
- Difficulty Speaking: Trouble finding the right words or forming sentences.
- Trouble Understanding Speech: Difficulty comprehending spoken language.
- Impaired Writing Skills: Difficulty expressing thoughts through writing.
- Challenges with Numerical Concepts: Difficulty with basic math skills.
- Reading Problems: Difficulty recognizing words or understanding written text.
- Social Awkwardness: Difficulty understanding social cues or norms.
- Inability to Recognize Faces: Difficulty remembering or recognizing faces.
- Poor Coordination: Difficulty with precise movements, like using utensils.
- Memory Problems: Difficulty recalling information or events.
- Difficulty with Problem-Solving: Trouble with logical reasoning or problem-solving skills.
Diagnostic Tests for Supramarginal Gyrus Disorders:
- Neurological Examination: Assessing reflexes, coordination, and sensory perception.
- Brain Imaging: MRI or CT scans to visualize brain structures.
- Language Assessments: Tests to evaluate language comprehension and expression.
- Cognitive Testing: Assessing memory, attention, and executive function.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): Recording brain wave patterns to detect abnormalities.
- Genetic Testing: Identifying genetic markers associated with neurological disorders.
- Blood Tests: Screening for metabolic or infectious causes of symptoms.
- Neuropsychological Assessment: Evaluating cognitive function and behavior.
- Functional MRI (fMRI): Mapping brain activity during specific tasks.
- Speech and Language Evaluation: Assessing speech production and comprehension abilities.
Treatments for Supramarginal Gyrus Disorders
(Non-Pharmacological):
- Speech Therapy: Exercises to improve language skills.
- Occupational Therapy: Activities to improve coordination and daily living skills.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Addressing cognitive and behavioral challenges.
- Social Skills Training: Learning appropriate social behaviors and interactions.
- Educational Support: Individualized education plans for children with learning difficulties.
- Assistive Technology: Devices to aid communication or daily tasks.
- Behavioral Interventions: Strategies to manage challenging behaviors.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Coping strategies for stress and anxiety.
- Environmental Modifications: Adjustments to home or work environments for better function.
- Family Support and Counseling: Helping families cope with the challenges of a loved one’s condition.
Medications for Supramarginal Gyrus Disorders:
- Antidepressants: To manage symptoms of depression or anxiety.
- Stimulants: Sometimes prescribed for attention deficits.
- Anticonvulsants: To control seizures in certain conditions.
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Used in some cases of cognitive decline.
- Dopamine Agonists: For management of movement disorders.
- Anxiolytics: Medications to reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Memory Enhancers: Drugs aimed at improving memory function.
- Antipsychotics: Used in some cases of severe behavioral disturbances.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Medications: To improve focus and attention.
- Sleep Aids: Sometimes prescribed for sleep disturbances related to the disorder.
Surgeries for Supramarginal Gyrus Disorders:
- Brain Tumor Resection: Surgical removal of tumors affecting the supramarginal gyrus.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Electrical stimulation of brain areas to modulate function.
- Epilepsy Surgery: Procedures to remove or disconnect areas of the brain causing seizures.
- Hemispherectomy: Removal or disconnection of one hemisphere of the brain in severe cases.
- Cortical Mapping: Surgical technique to identify and preserve critical brain areas during surgery.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): Implantation of a device to treat epilepsy or depression.
- Lesionectomy: Surgical removal of a specific brain lesion causing symptoms.
- Cerebral Angioplasty and Stenting: Procedures to restore blood flow in blocked brain vessels.
- Functional Neurosurgery: Targeted surgeries to modulate brain function in specific areas.
- Cerebral Shunt Placement: Surgical placement of a shunt to drain excess fluid from the brain.
Preventive Measures for Supramarginal Gyrus Disorders:
- Protective Headgear: Use helmets during activities with a risk of head injury.
- Regular Exercise: Promotes overall brain health and reduces the risk of stroke.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet supports brain function and overall well-being.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Control conditions like diabetes or hypertension to reduce stroke risk.
- Avoid Toxins: Minimize exposure to environmental toxins or substances harmful to the brain.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Monitor health status and address any emerging issues promptly.
- Cognitive Stimulation: Engage in activities that challenge and stimulate the brain.
- Stress Management: Practice techniques to reduce stress and promote relaxation.
- Genetic Counseling: For individuals with a family history
Disclaimer: Each person’s journey is unique, treatment plan, life style, food habit, hormonal condition, immune system, chronic disease condition, geological location, weather and previous medical history is also unique. So always seek the best advice from a qualified medical professional or health care provider before trying any treatments to ensure to find out the best plan for you. This guide is for general information and educational purposes only. If you or someone are suffering from this disease condition bookmark this website or share with someone who might find it useful! Boost your knowledge and stay ahead in your health journey. Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the article.