Organomegaly means an internal organ is bigger than normal. The word comes from “organo” (organ) and “megaly” (big). Any organ can become large. The most ...
“Phakomatoses” (also called neurocutaneous syndromes) are conditions that affect the skin, the brain and nerves, and often other organs. The word comes from an ...
Moyamoya disease is a rare brain blood vessel problem where the main arteries that carry blood into the deep parts of the brain slowly become tight and narrow. ...
This phrase means all the eye problems and eye changes that can happen because of isotretinoin. Isotretinoin is a vitamin A–like drug (a retinoid) that shrinks ...
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a long-lasting skin disease. It causes painful lumps, boils, and “tunnels” under the skin. These bumps happen where skin rubs ...
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a dangerous “immune storm.” The body’s defender cells (T cells, NK cells, and macrophages) get stuck in the ON ...
Iron-Overloaded Syndrome means too much iron builds up in the body over time. Iron is essential for life. We need iron to make hemoglobin, which carries oxygen ...
Hemochromatosis is a condition where the body stores too much iron over many years. Iron is a normal mineral that helps make blood and carry oxygen. In ...
Freeman–Sheldon syndrome (also called Freeman–Burian syndrome or distal arthrogryposis type 2A) is a very rare condition that starts before birth. It mainly ...
Ectodermal dysplasia (ED) is a group of inherited conditions that affect body parts that grow from the ectoderm, which is the outer layer of the early embryo. ...
Chiari malformations are conditions where parts of the brain at the back of the head sit lower than they should. In Chiari I, the lower part of the cerebellum ...
Bosma Arrhinia Microphthalmia Syndrome (BAMS) is a very rare genetic condition. Babies are born with a missing or very under-developed nose (this is called ...
Alzheimer’s disease is best known as a brain disease that causes memory loss. The eyes and the visual system are part of the nervous system too. The retina is ...
Alkaptonuria (AKU) is a rare, inherited metabolic disease. It happens when the body cannot break down a chemical called homogentisic acid (HGA). This problem ...
Ocular Ischemic Syndrome (OIS) is a serious eye condition that happens when the eye does not get enough blood and oxygen for a long time. In simple words, the ...
Cosmetic lasers and light-based beauty devices are used for hair removal, skin resurfacing, tattoo removal, acne scars, blood vessels, and wrinkles. These ...
Ocular graft-versus-host disease (oGVHD) is an eye problem that can happen only after an allogeneic stem cell or bone marrow transplant. In this transplant, ...
Ocular Features of Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) is a group of rare, inherited conditions where certain long sugar chains called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) build ...
A craniopharyngioma is a slow-growing, benign brain tumor that usually sits above the pituitary gland and next to the optic chiasm (the crossing of the optic ...
Ocular discomfort is any unpleasant feeling on the surface of the eye or around the eyelids. It can feel dry, sandy, scratchy, itchy, hot, burning, watery, ...
Ocular decompression retinopathy (ODR) is an eye problem that can happen after eye pressure drops very quickly. Eye doctors call eye pressure “intraocular ...
Ocular candidiasis means a yeast infection in or on the eye. The yeast is most often Candida. The common species is Candida albicans, but other species like C. ...
An ocular bee injury means a bee or similar insect has harmed the eye or the tissues around the eye. The harm can be from a sting, from the stinger staying in ...
Ocular anesthesia–induced injury is harm to the eye or the area around the eye caused by the way eye anesthesia is given or by the anesthetic drug itself. Eye ...
Ocular amyloidosis means “amyloid” protein builds up in parts of the eye. Amyloid is a mis-folded protein that the body cannot clear well. Over time, the extra ...
Occult macular dystrophy is a rare, inherited eye condition that causes gradual loss of central vision even though the front and back of the eye can look ...
Occipital neuralgia is a pain problem that involves the greater, lesser, or third occipital nerves. These nerves start in the upper neck (mostly from the C2 ...
Occipital epilepsy is a kind of focal (partial) epilepsy that starts in the occipital lobes, which sit at the back of the brain and handle vision. Because the ...
Nystagmus means the eyes move on their own, back and forth, up and down, or in a small circular twist, even when you are trying to keep them still. The ...
Nutritional optic neuropathy (often shortened to NON) is a problem in the optic nerve that happens when the body does not get, absorb, or use certain key ...
North Carolina Macular Dystrophy (NCMD) is a rare, inherited eye condition that affects the macula, the small central area of the retina that we use for sharp, ...
Norrie disease is a rare genetic condition. It mostly affects boys and men. It usually causes very poor vision or complete blindness at birth or soon after ...
Normal-tension glaucoma is a kind of glaucoma where the optic nerve is damaged even though your measured eye pressure is in the “normal” range. The eye’s ...
Noonan syndrome is a genetic condition. It affects many parts of the body. It changes how a child grows and develops. It often causes a special look to the ...
Orbital pseudotumor is inflammation that happens inside the eye socket (the “orbit”) without a proven infection or cancer. It is called “pseudo-tumor” because ...
Orbital Inflammatory Syndrome means there is swelling and inflammation inside the eye socket, which doctors call the orbit. The orbit holds the eye, the eye ...
Idiopathic orbital inflammation is an inflammatory disease inside the eye socket (the “orbit”) where no infection, tumor, or named systemic disease can be ...
Nonspecific orbital inflammation (NSOI) is swelling and irritation that happens inside the eye socket (the “orbit”) for reasons that are not clearly known. ...
Nonparetic diplopia means you see two images at the same time, but not because a nerve or eye muscle is paralyzed. instead, the eyes (or the optical system of ...
Non-paraneoplastic autoimmune retinopathy (npAIR) is an eye disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the retina. The retina is the ...
Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, or NAION, is a sudden drop in vision that happens because the front part of the optic nerve does not get ...
Nocardia eye” means an eye infection caused by Nocardia bacteria. It most often affects the cornea (the clear front window of the eye) and can sometimes ...
Neurotrophic keratitis is an eye surface disease caused by poor corneal nerve function. The clear front window of the eye is called the cornea. The cornea ...
Neurosarcoidosis is sarcoidosis that involves the nervous system. Sarcoidosis is an immune condition where small clusters of inflammatory cells, called ...
Neuroretinitis is an eye problem where the optic nerve (the cable that carries visual signals to your brain) becomes inflamed, and fluid leaks into the central ...
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a group of rare eye disorders that slowly damage the light‑sensing cells in the retina. The retina is the thin film at the back of ...
Neuropathy means damage or disease of nerves. Nerves are the body’s electrical cables. They carry feeling (touch, temperature, pain), control muscles ...
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is an autoimmune disease. This means the body’s defense system, which usually protects you from germs, ...
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is an autoimmune disease. “Autoimmune” means your immune system, which normally protects you, mistakenly attacks ...
Neurofibromatosis is a group of genetic conditions. In these conditions, small mistakes in certain genes make cells in nerves grow in the wrong way. This can ...
Neuroferritinopathy is a rare brain disorder where iron slowly builds up inside movement-control areas of the brain, especially the basal ganglia. The iron ...
Neuroblastoma is a cancer that starts in very young nerve cells. These young nerve cells are called “neuroblasts.” They are baby cells of the sympathetic ...
Neurodegeneration in diabetic retinopathy means the nerve cells in the retina start getting sick and dying because of diabetes—even before the classic “leaky ...
In normal life, tiny brain arteries feed the deep brain. If those vessels get sick or narrow, blood flow is not steady. Little clots may form. The brain wiring ...
CADASIL is a genetic small-vessel disease of the brain. It is caused by a harmful change (a “pathogenic variant”) in a gene called NOTCH3. This gene sits on ...
Bilingual aphasia is a language problem that happens after brain injury in a person who uses two languages.Aphasia means trouble using or understanding ...
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy is a brain blood-vessel problem. In CAA, tiny proteins called amyloid-beta (Aβ) build up in the walls of small and medium arteries ...
A ganglioglioma is a rare brain or spinal cord tumor. It has two parts in the same lump. One part is made of nerve cells (ganglion cells). The other part is ...
Choroid plexus papilloma (CPP) is a rare, usually benign (non-cancer) brain tumor that starts in the choroid plexus, the spongy tissue inside the brain’s fluid ...
Pilomyxoid astrocytoma is a rare brain tumor that starts from star-shaped support cells in the brain called astrocytes. Doctors first recognized it as a tumor ...
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS) is a breathing disorder that happens in people with obesity who do not breathe out enough carbon dioxide (CO₂) while ...
Ragged red fibers are not a single disease by themselves, but a very important clue that doctors sometimes see when they look at a tiny piece of muscle under a ...
Myoclonic epilepsy is a condition where the brain sends sudden, extra “spark” signals that make a muscle, or a group of muscles, jerk for a brief moment. The ...
Lymphocytic hypophysitis is inflammation of the pituitary gland caused by the body’s own immune system. The pituitary is a tiny “master gland” at the base of ...
Hypertrophic pachymeningitis (HP) means the dura mater—the tough outer covering of the brain and spinal cord—gets abnormally thick and inflamed. Hypertrophic ...
Anti-GAD antibody syndrome is an umbrella term for autoimmune conditions in which your immune system makes antibodies against an enzyme called glutamic acid ...
Neuro-ophthalmologic manifestations of ALS are the eye and vision problems that come from changes in the brain and nerves that control eye movement, eyelids, ...
Latent Autoimmune Diabetes of Adults, or LADA, is a type of diabetes that starts in adulthood and is driven by the immune system. In LADA, the immune system ...
The thalamus is a deep, egg-shaped structure on each side of the brain. It acts like a relay and traffic controller for many signals that go to and from the ...
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy—usually shortened to PML—is a rare, serious brain disease. It happens when a very common virus called the JC virus ...
Primary Sjögren Syndrome is a long-term autoimmune disease. “Autoimmune” means your immune system—your body’s defense—mistakenly attacks your own tissues. In ...
A cough-induced rib fracture happens when repeated, forceful coughing (or one severe cough) places very high stress on the rib cage. The muscles between the ...
Post-concussion syndrome means symptoms that keep going after a concussion. A concussion is a mild brain injury from a hit, jolt, or rapid shaking of the head. ...
Polyarteritis nodosa is a disease where the body’s immune system attacks medium-sized and some small arteries. These arteries become inflamed and damaged. The ...
Pneumosinus dilatans is when one or more of the air spaces in the face (the paranasal sinuses) get bigger than normal and are filled with air, but the bony ...
Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) is a rare brain disease. It damages parts of the brain that control movement, balance, and automatic body functions like blood ...
Mollaret meningitis is a rare, recurrent form of “aseptic” meningitis. “Aseptic” means the spinal fluid is inflamed but standard bacterial cultures are ...
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune nerve-to-muscle junction problem. Your immune system makes antibodies that sit on tiny calcium ...
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is an aggressive brain cancer that grows quickly and spreads into nearby brain tissue. It is the most common malignant brain ...
Familial Dysautonomia (also called Riley–Day syndrome or hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type III) is a rare condition that children are born with. ...
Cryptococcal meningitis is a serious brain and spinal cord infection caused by a yeast (a type of fungus) called Cryptococcus. The fungus loves to live in the ...
A colloid brain cyst is a small, round, fluid-filled sac that usually sits in the front part of the third ventricle of the brain, right next to the foramen of ...
The basilar artery is a large artery at the back of the brain. It forms where the two vertebral arteries join in front of the brainstem, then runs upward to ...
Chordoma is a rare bone cancer that grows from leftover notochord tissue along the spine and skull base; when it forms at the skull base (the clivus), it can ...
Celiac disease is an immune reaction to gluten (a protein in wheat, barley, and rye). In some people, this immune reaction doesn’t stop at the gut. It can also ...
Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) is a kind of brain injury that mostly affects very premature babies. The injury happens in the white matter near the brain’s ...
Krabbe disease is a rare, inherited brain disease. It damages the white wiring of the brain and the nerves that carry signals. This damage happens because a ...
Neuhauser syndrome (MMR) is a congenital (present at birth) disorder. A baby is born with very large corneas. The cornea is the clear, front window of the eye. ...
Neovascular glaucoma happens when the retina does not get enough oxygen for a period of time (this is called retinal ischemia). In response, the eye releases a ...
Neonatal conjunctivitis means inflammation and discharge of the eye surface in a newborn baby during the first 28 days of life. The thin, clear skin that ...
Necrotizing herpetic retinitis is a serious eye infection that damages the retina. The retina is the thin, light-sensing layer at the back of the eye that lets ...
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the peritubular cells of the renal cortex. This hormone stimulates red blood cell production in ...
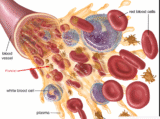
Early destruction of red blood cells (RBCs), also known as hemolysis, leads to hemolytic anemia, a condition where RBCs are destroyed faster than the ...
Necrotizing fasciitis is a very fast, very serious infection under the skin. It attacks the “fascia,” which is the thin but strong sheet that covers muscles, ...
Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma (NXG) is a very rare disease of the immune system that most often shows up in the skin, especially around the eyes. In this ...
The nasolacrimal duct is a tiny tube that carries tears from the eye into the nose. The duct starts at small openings on the eyelid edges called puncta. The ...
A naso-orbitoethmoid (NOE) complex fracture is a break of the thin bones in the middle of the face where the top of the nose meets the inner corner of the eye ...
Nanophthalmos is a rare eye condition where the eyeball is smaller than normal in all parts, but the basic parts of the eye are still built in the usual way. ...
Dermatochalasis means “too much skin” on the eyelids—most often the upper lids—so the skin drapes or “hoods” over the natural eyelid crease. It happens mainly ...
Blepharoptosis, often shortened to ptosis, means the upper eyelid hangs lower than normal. In plain terms: the top eyelid droops and may cover part of the ...
Müller’s Muscle–Conjunctival Resection—often shortened to MMCR—is a small, inside-the-eyelid operation used to lift a mildly droopy upper eyelid (ptosis). The ...
Möbius syndrome (Moebius syndrome) is a rare condition present at birth. It mainly affects the 6th (abducens) and 7th (facial) cranial nerves. Because these ...
Myopic traction maculopathy (MTM) is a problem that happens in some people with high (pathologic) myopia. The very back of the eye (the macula, which you use ...
Myopic choroidal neovascular membrane (myopic CNVM) is a condition where abnormal blood vessels grow beneath the retina in individuals with high myopia, also ...
Myopia of prematurity is nearsightedness that starts very early in babies born too soon. In myopia, distant objects look blurry because the eye focuses light ...
Myopia (also called nearsightedness) means distant objects look blurry while near objects look clear. In very simple terms, the eye’s built-in focusing system ...
Myogenic ptosis means the upper eyelid droops because the levator palpebrae superioris muscle (the main “lid-lifting” muscle) is weak, stiff, or poorly formed. ...
Myelinated retinal nerve fiber layer means the insulating “white coating” (myelin) that normally stops at the back of the eye has grown a little farther ...
Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein (MOG) is a small protein that sits on the outer surface of that myelin. In MOG-optic neuritis, the immune system mistakenly ...
A mycotic ulcer is an open, painful sore on the cornea (the clear, dome-shaped “window” at the front of your eye) that is caused by a fungus. “Mycotic” means ...
Mucositis means inflammation and injury of the mucous membranes. Mucous membranes are the soft, moist linings inside the mouth, throat, esophagus (food pipe), ...
A mycoplasma-induced rash is a skin and mucous-membrane reaction that happens during or soon after infection with the germ Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Many people ...